111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

水溶性 C60 可防止博来霉素诱导的小鼠肺纤维化
Authors Dong R, Liu M, Huang XX, Liu Z, Jiang DY, Xiao HJ, Geng J, Ren YH, Dai HP
Received 1 May 2019
Accepted for publication 16 December 2019
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2269—2276
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S214056
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, fibrotic interstitial pneumonia. And, oxidation/antioxidant imbalance plays an important role in the progress of IPF. Fullerene is considered to be a novel “structural” antioxidant. This study aimed to explore if water-soluble C60 (C60(OH)22) can exhibit antifibrotic activity in its antioxidant role.
Methods: Healthy C57BL/6J mice were randomly grouped and induced pulmonary fibrosis by intratracheal injection of bleomycin.
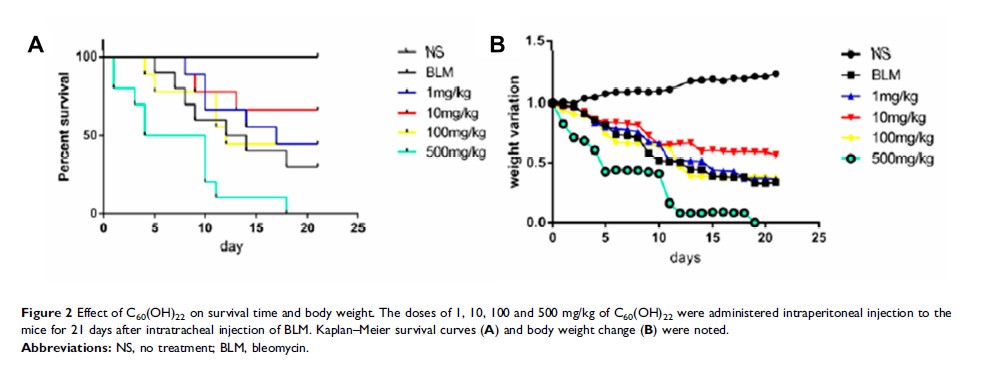
Results: The survival rate of mice was observed and found that 10mg/kg was the optimal dose of water-soluble C60 for pulmonary fibrosis. We observed that water-soluble C60 can alleviate the severity of pulmonary fibrosis by observing the chest computed tomography, pulmonary pathology, and content of collagen, alpha smooth muscle actin and fibronectin in lung. Compared with bleomycin group, ROS, the content of TNF-α in BALF, and the number of fibroblasts was significantly decreased and the number of type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells was increased after treatment with C60.
Conclusion: Therefore, thanks to its powerful antioxidant action, water-soluble C60 can reduce the severity of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice.
Keywords: pulmonary fibrosis, bleomycin, water-soluble C60, mice