111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

线粒体调节的多孔 Se@SiO2 纳米颗粒可保护气道上皮细胞免受氧化损伤:对急性肺损伤的意义
Authors Wang M, Wang K, Deng G, Liu X, Wu X, Hu H, Zhang Y, Gao W, Li Q
Received 28 November 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2287—2302
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S240301
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Shen
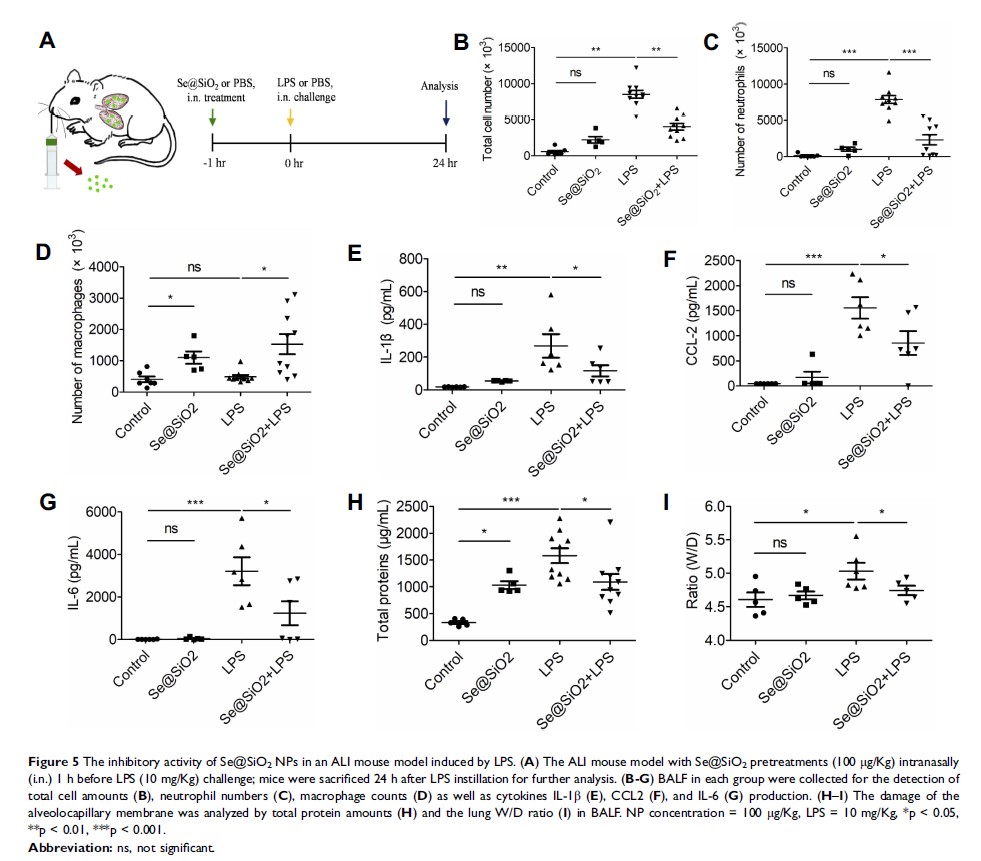
Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction played a vital role in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including acute lung injury (ALI). However, few strategies targeting mitochondria were developed in treating ALI. Recently, we fabricated a porous Se@SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) with antioxidant properties.
Methods: The protective effect of Se@SiO2 NPs was assessed using confocal imaging, immunoblotting, RNA-seq, mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) activity assay, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) in airway epithelial cell line (Beas-2B). The in vivo efficacy of Se@SiO2 NPs was evaluated in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI mouse model.
Results: This study demonstrated that Se@SiO2 NPs significantly increased the resistance of airway epithelial cells under oxidative injury and shifted lipopolysaccharide-induced gene expression profile closer to the untreated controls. The cytoprotection of Se@SiO2 was found to be achieved by maintaining mitochondrial function, activity, and dynamics. In an animal model of ALI, pretreated with the NPs improved mitochondrial dysfunction, thus reducing inflammatory responses and diffuse damage in lung tissues. Additionally, RNA-seq analysis provided evidence for the broad modulatory activity of our Se@SiO2 NPs in various metabolic disorders and inflammatory diseases.
Conclusion: This study brought new insights into mitochondria-targeting bioactive NPs, with application potential in curing ALI or other human mitochondria-related disorders.
Keywords: mitochondrial dysfunction, porous Se@SiO2 nanoparticles, acute lung injury, anti-oxidative injury, anti-inflammation