111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NK4 偶联羟基喜树碱脂质体的制备、表征和体内评价
Authors Zhou T, Zhang W, Cheng D, Tang X, Feng J, Wu W
Received 25 December 2019
Accepted for publication 9 March 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2277—2286
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S243746
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
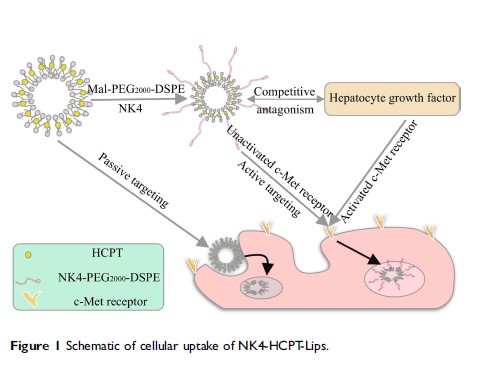
Purpose: In this study, NK4-conjugated hydroxycamptothecin liposomes (NK4-HCPT-Lips) were prepared with the aim of improving drug targeting to the liver.
Methods: NK4-HCPT-Lips were prepared using the thin-film dispersion method. In vitro antitumor activities were evaluated by MTT assay. HCPT levels in plasma and tissues were determined via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with camptothecin as the internal standard, and the characteristics, pharmacokinetics, and bio-distribution of NK4-HCPT-Lips were evaluated.
Results: The liposomes showed a regular spherical-shaped morphology, and the entrapment efficiency and drug loading capacity reached 82.5 ± 2.4% and 3.01 ± 0.23%, respectively, with a particle size of 155.6 ± 2.6 nm and a zeta potential of − 24.8 ± 3.3 mV. Inhibition effect experiments found that NK4-HCPT-Lips had a good inhibition on the HepG2 cells. Pharmacokinetic studies revealed an increase in the area under the curve and mean residence time as well as a decrease in plasma clearance (p < 0.05) of the NK4-HCPT-Lips compared to those of HCPT liposomes and a commercial HCPT injection. Tissue distribution studies showed that NK4-HCPT-Lips were present at high levels in the liver but were cleared from the kidneys.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that NK4-HCPT-Lips possess excellent liver-targeting attributes, which could enhance the therapeutic effects of drug treatments for hepatic diseases.
Keywords: hydroxycamptothecin, NK4, liposomes, pharmacokinetics, bio-distribution