111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

银杏二萜内酯通过 NT3-TrkA 和 Ras-MAPK 途径发挥抗抑郁作用
Authors Wang T, Bai S, Wang W, Chen Z, Chen J, Liang Z, Qi X, Shen H, Xie P
Received 29 August 2019
Accepted for publication 16 March 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1279—1294
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S229145
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
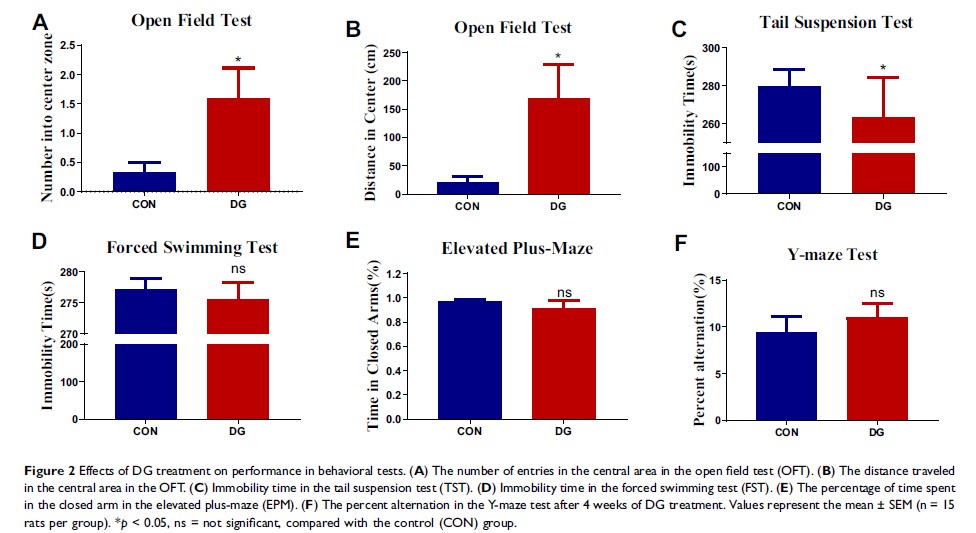
Background: Depression is a highly prevalent mental illness that severely impacts the quality of life of affected individuals. Our recent studies demonstrated that diterpene ginkgolides (DG) have antidepressant effects in mice. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remained much unclear.
Methods: In this study, we assessed the antidepressant effects of chronic DG therapy in rats by evaluating depression-related behaviors, we also examined potential side effects using biochemical indicators. Furthermore, we performed an in-depth molecular network analysis of gene–protein–metabolite interactions on the basis of metabolomics.
Results: Chronic DG treatment significantly ameliorated the depressive-like behavioral phenotype. Furthermore, the neurotrophin signaling-related NT3-TrkA and Ras-MAPK pathways may play an important role in the antidepressant effect of DG in the hippocampus.
Conclusion: These findings provide novel insight into the mechanisms underlying the antidepressant action of DG, and should help advance the development of new therapeutic strategies for depression.
Keywords: diterpene ginkgolides, antidepressant, neurotrophin, hippocampus, NT3-TrkA and Ras-MAPK pathways