111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

羧肽酶 X(M14 家族 2)的表达通过调节 gp130/JAK2/Stat1 信号通路加速肝细胞癌的进展
Authors Ye Y, An Y, Wang M, Liu H, Guan L, Wang Z, Li W
Received 28 August 2019
Accepted for publication 17 February 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2353—2364
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S228984
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Carboxypeptidase X, M14 family member 2 (CPXM2) has been reported to be involved with several human malignancies. However, the impact of CPXM2 on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumorigenesis has not been studied.
Materials and Methods: Using immunohistochemistry, the detailed CPXM2 expression patterns were examined in HCC cell lines and tissues. Additionally, a hepatic stellate cell line overexpressing CPXM2 and an HCC CPXM2-knockdown cell line were established by lipofection of an expression plasmid or short hairpin RNA, respectively. The transfection efficiencies were confirmed by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, Western blotting and immunofluorescence. Moreover, Western blotting was conducted to determine the phosphorylation levels of the tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat1) pathway. Furthermore, gp130-specific hairpin RNA was used to knockdown gp130 expression in hepatic stellate cells overexpressing CPXM2. The malignant phenotype of cultured HCC cells was assessed by a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assay, plate cloning assay, Matrigel invasion assay and wound-healing assay in vitro.
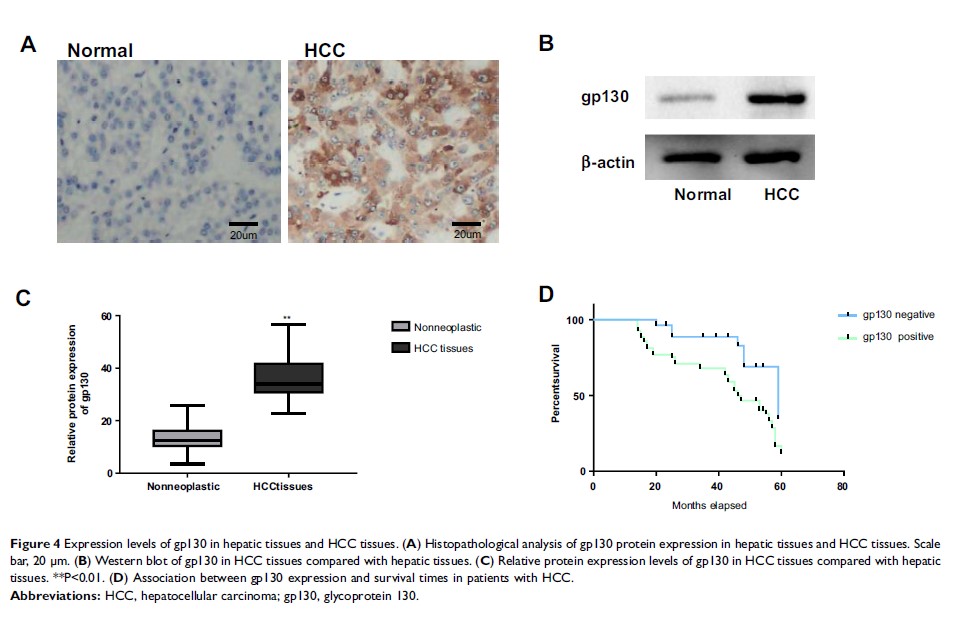
Results: It was demonstrated that CPXM2 was upregulated in HCC, and its upregulation predicted a poor prognosis. Besides, the upregulation of CPXM2 markedly enhanced the metastatic potential of HCC via the gp130/JAK2/Stat1 signaling pathway in vitro.
Conclusion: In summary, this evidence suggests a positive role for CPXM2 in HCC progression via modulation of the gp130/JAK2/Stat1 signaling pathway in HCC.
Keywords: carboxypeptidase XM14 family member 2, hepatocellular carcinoma, metastasis