111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PCR-反向斑点杂交技术用于人乳头瘤病毒基因分型试验,及对中国患者 CIN 2+ 手术后残留/复发进行评估
Authors Zhang Q, Dong B, Chen L, Lin T, Tong Y, Lin W, Lin H, Gao Y, Lin F, Sun P
Received 6 November 2019
Accepted for publication 13 March 2020
Published 1 April 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2369—2379
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S237490
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
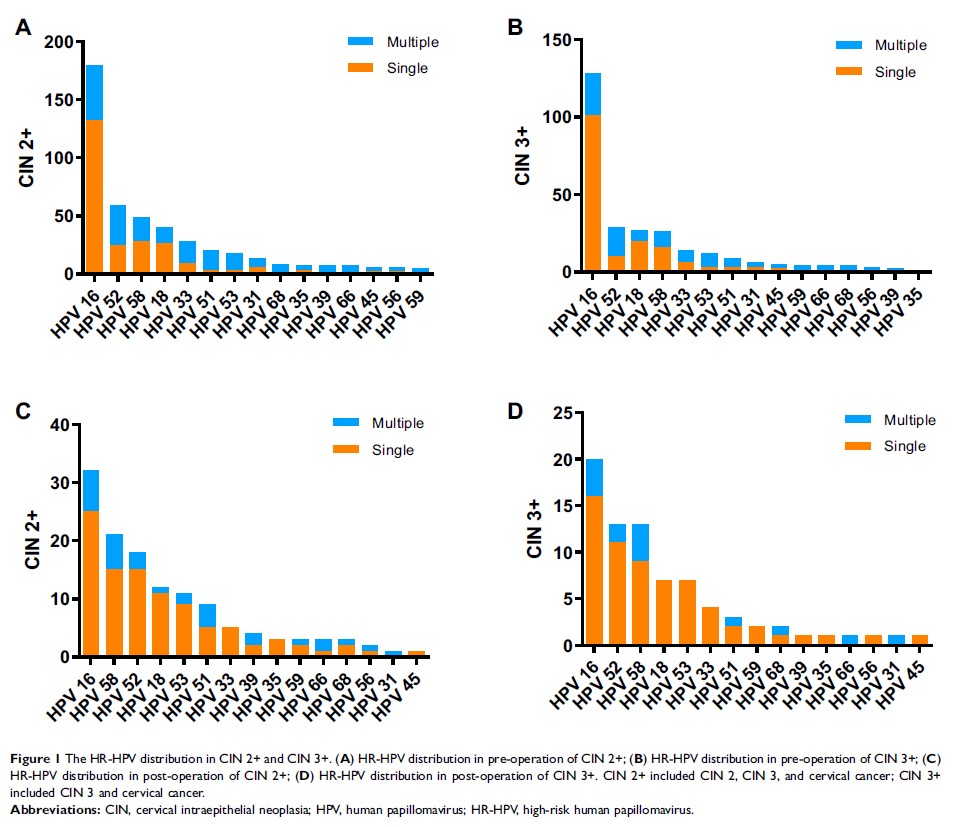
Objective: To assess the clinical value of the PCR-reverse dot blot human papillomavirus genotyping test during follow-up of patients with CIN grade 2 or worse (CIN 2+).
Methods: Four hundred patients with CIN 2+ receiving treatment from January 2008 to January 2017 were included in our study. Postoperative follow-up procedures comprised HPV examination and cervical cytology every 3– 6 months for the first 2 years and then followed up every 6– 12 months. A pathology examination was performed when there was a positive funding for HPV 16/18 or an abnormal ThinPrep cytology test (TCT) with or without positive for HR-HPV according to the American Society for Coloscopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) guidelines.
Results: The median follow-up period was 27.10± 12.47 months (ranging from 3 to 50 months). During follow-up, 12.00% (48/400) of the women developed residual/recurrent disease. The highest risk in CIN 2+ and CIN 3+ residual/recurrence was HPV-16/-18 (hazard ratio (HR)=12.898, 95% CI= 6.849– 24.289; HR= 20.726, 95% CI= 9.64– 44.562, respectively). Among the different follow-up methods, type-specific (TP) HR-HPV persistent infection showed the highest cumulative incidence risk (CIR) (84.62%, 95% CI=73.29– 95.94) and HR (5.38, 95% CI= 2.596– 11.149) during the 4-year follow-up period. At the CIN 2+ and CIN 3+ endpoints, TP-HPV testing had relatively high sensitivity (84.62%, 95% CI=73.29– 95.94 and 89.28%, 95% CI= 77.83– 100.00, respectively) and specificity (78.07%, 95% CI= 72.70– 83.44 and 75.73%, 95% CI= 70.30– 81.17, respectively). However, at the CIN 2+/CIN 3+ endpoint, TCT follow-up had a sensitivity of 60.42%/62.16% (95% CI=46.58– 72.25/46.54– 77.79) and specificity of 90.18%/88.72% (95% CI=86.95– 93.41/85.35– 92.10).
Conclusion: TP HR-HPV follow-up can provide a reliable and sensitive clinical reference for CIN 2+ postoperative patients.
Keywords: papillomavirus, genotype, cell biology, histology, postoperative