111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA HOTTIP 通过调节 miR-137 在胰腺癌中的表达参与肿瘤细胞的顺铂耐药性
Authors Yin F, Zhang Q, Dong Z, Hu J, Ma Z
Received 16 October 2019
Accepted for publication 13 December 2019
Published 1 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2689—2699
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234924
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the effect of HOTTIP and miR-137 on cisplatin resistance of pancreatic cancer cells, and study the mechanism of the effect of HOTTIP on the resistance to cisplatin in pancreatic cancer cells, so as to provide new targets for clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Methods: Pancreatic cancer cells were induced to be resistant to cisplatin by gradually increasing cisplatin concentration at a low concentration gradient in vitro. The changes of HOTTIP and miR-137 were detected, and the effects of HOTTIP and miR-137 on cisplatin efficacy of pancreatic cancer cisplatin-resistant cells were analyzed to explore the mechanism of HOTTIP on cisplatin resistance of pancreatic cancer cells.
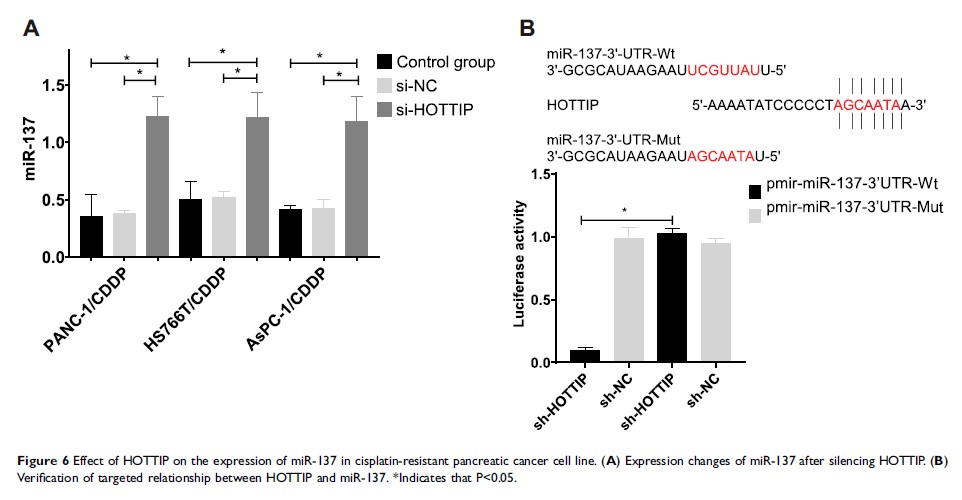
Results: After inducing cisplatin resistance in pancreatic cancer cells, the expression level of HOTTIP in pancreatic cancer cells further increased and miR-137 decreased. Silencing HOTTIP or over-expression of miR-137 can increase the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cisplatin-resistant cells to cisplatin, inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells, and promote apoptosis. And we found HOTTIP can target to inhibit miR-137 expression. Rescue experiments showed that regulating miR-137 cannot affect the expression of HOTTIP, miR-137 is a downstream target of HOTTIP, and down-regulation of miR-137 expression can obviously hinder the cisplatin sensitization effect of silencing HOTTIP on cisplatin-resistant pancreatic cancer cells.
Conclusion: Silencing HOTTIP reverses cisplatin resistance of pancreatic cancer cells by promoting miR-137 expression.
Keywords: IncRNA HOTTIP, miR-137, pancreatic cancer, cisplatin, drug resistance, targeted therapy