111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抑制 EGFR 信号转导及激活线粒体凋亡有助于丹参酮 IIA 介导的非小细胞肺癌细胞的肿瘤抑制
Authors Gao F, Li M, Liu W, Li W
Received 19 January 2020
Accepted for publication 14 March 2020
Published 2 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2757—2769
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S246606
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
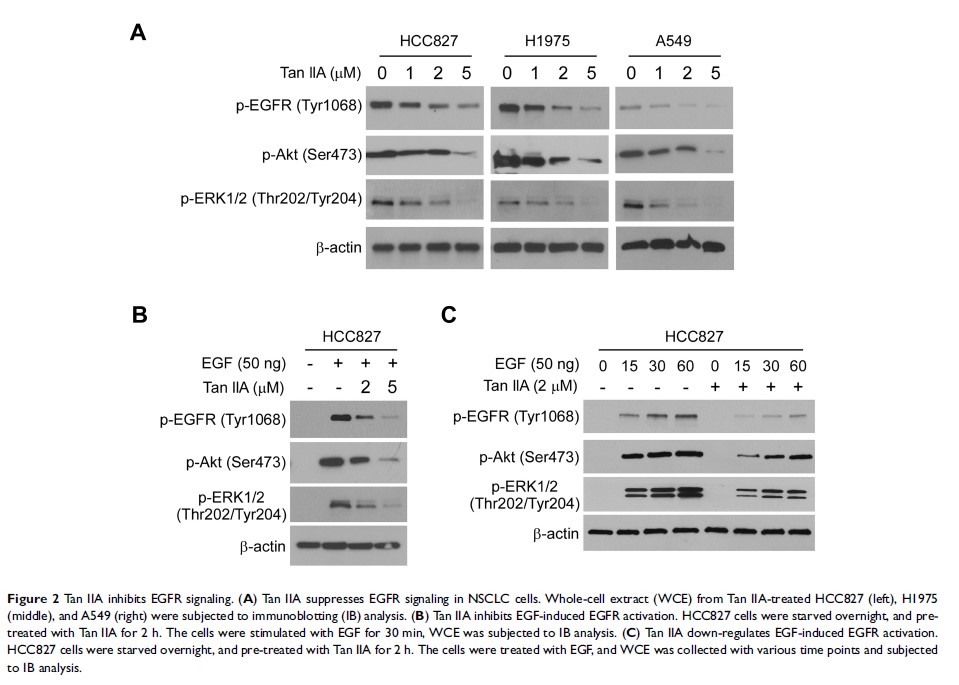
Background: Deregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling plays a critical role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis. The natural product Tanshinone IIA (Tan IIA) exhibits significant anti-tumor effect in various human cancers, however, the mechanism remains elusive.
Methods: The inhibitory effect of Tan IIA NSCLC cells was determined by MTS and soft agar assays. The activation of EGFR signaling and the protein level of myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1) were examined by immunoblot (IB), immunohistochemical staining (IHC), and ubiquitination analysis. The in vivo anti-tumor effect was validated by the xenograft mouse model.
Results: Tan IIA inhibits NSCLC cells through suppression of EGFR signaling. Tan IIA decreases cell viability and colony formation in EGFR wild type and activating mutant cell lines. The IB data further confirmed that Tan IIA suppresses EGFR phosphorylation time- and dose-dependently. Tan IIA destabilizes Mcl-1 and shortens the half-life. Ubiquitination analysis showed that treatment with Tan IIA promotes Mcl-1 ubiquitination and degradation. Further study showed that the downregulation of EGFR-Akt signaling is required for Tan IIA-induced Mcl-1 reduction. Ectopic overexpression of constitutively activated Akt1 compromised these antitumor efficacies in Tan IIA-treated NSCLC cells. Finally, Tan IIA inhibited the in vivo tumor growth.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that Tan IIA acts as an EGFR signaling inhibitor, and targeting EGFR-Akt-Mcl1 axis could provide a new option for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, Tanshinone IIA, epidermal growth factor receptor, Mcl-1, ubiquitination