111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-499a-5p 通过靶向 eIF4E 抑制 Pr5/4/20 发布的癌细胞
Authors Gu X, Dong M, Liu Z, Yang J, Shi Y
Received 9 December 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 5 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2913—2924
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S241631
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Introduction: The present study aimed to explore the role of miR-499a-5p and its molecular mechanism in cervical cancer (CC).
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR) and Western blotting were performed to detect the expression of miR-499a-5p and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in CC tissues and cell lines. The proliferation, migration, and invasion of CC cells were detected by MTT assay, wound healing assay, and Transwell assay. Apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry and alterations of apoptosis-related genes. The effect of miR-499a-5p on epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) was examined by determining the protein levels of EMT-associated genes. Then, colony formation assay was used to determine the radiosensitivity of CC cells. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to confirm the direct target of miR-499a-5p.
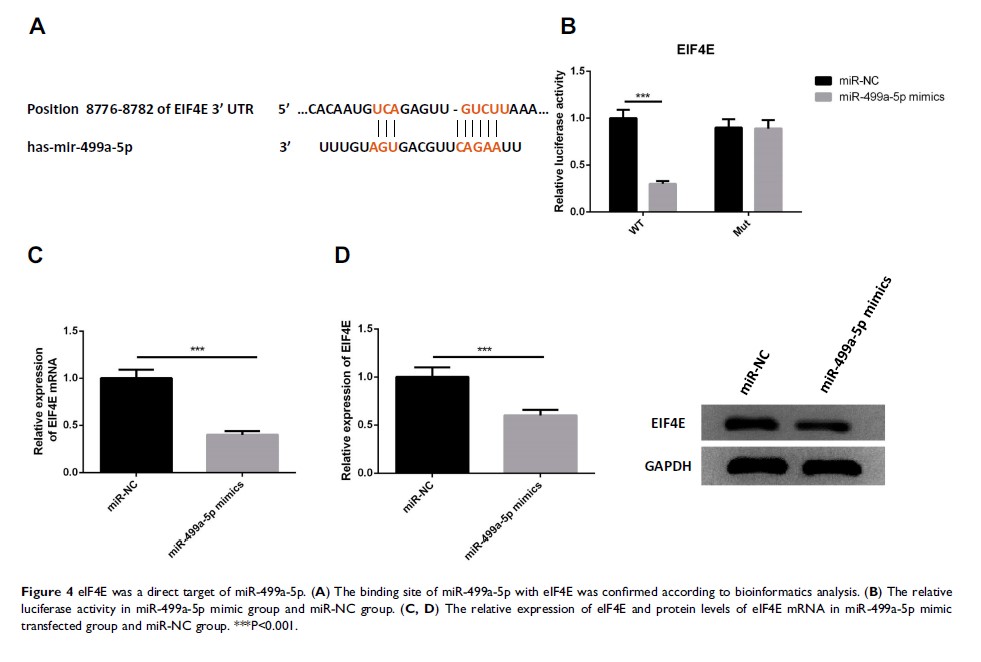
Results: MiR-499a-5p was significantly downregulated in CC tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-499a-5p or eIF4E knockdown markedly inhibited cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT, and enhanced apoptosis. eIF4E was predicted and verified as a target gene of miR-499a-5p. The influence of miR-499a-5p upregulation on proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration, EMT, and radiosensitivity was abrogated by eIF4E overexpression.
Discussion: MiR-499a-5p promoted the apoptosis and radiosensitivity and inhibited proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT by directly targeting eIF4E in CC cells.
Keywords: cervical cancer, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, miR-499a-5p, radiosensitivity