111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

有磺酸基团的大孔表面,及 PEEK/纳米硅酸镁复合材料的微纳米结构,表现出抗菌活性并诱导细胞反应
Authors Niu Y, Guo L, Hu F, Ren L, Zhou Q, Ru J, Wei J
Received 12 November 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 9 April 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2403—2417
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S238287
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: To improve the surface bio-properties of polyetheretherketone (PEEK)/nano magnesium silicate (n-MS) composite (PC).
Materials and Methods: The surface of PC was firstly treated by particle impact (PCP) and subsequently modified by concentrated sulfuric acid (PCPS).
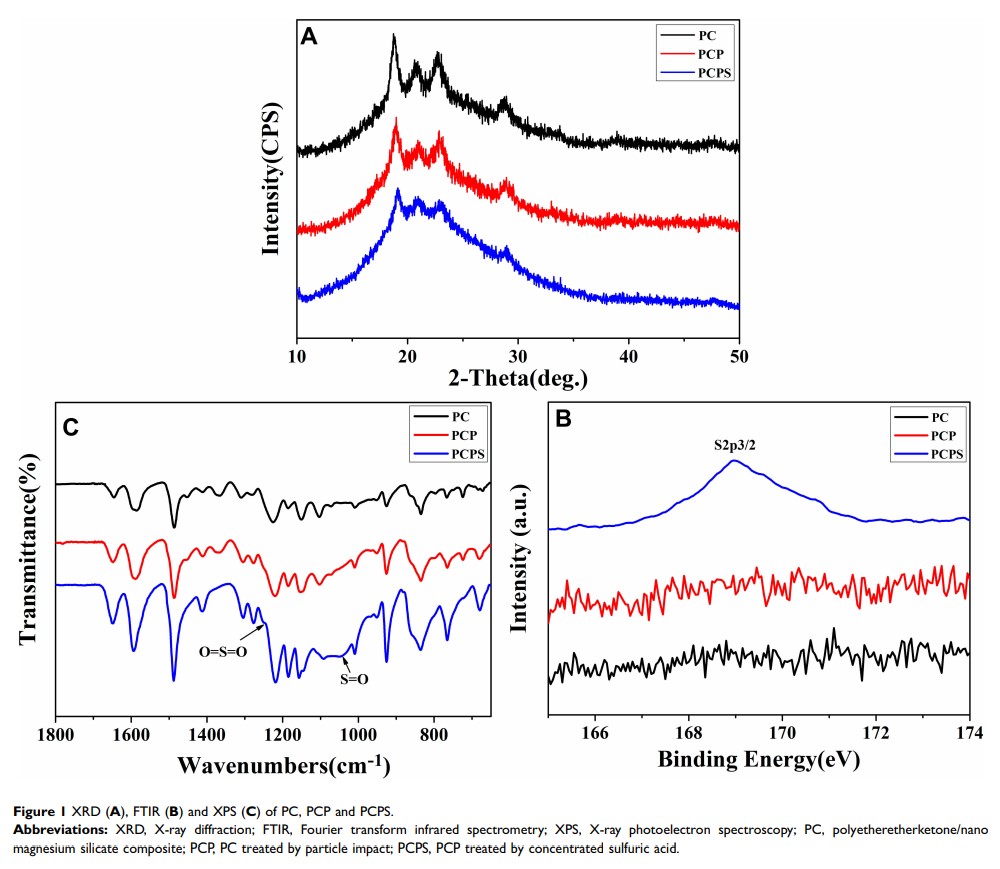
Results: PCPS surface exhibited not only macropores with sizes of about 150 μm (fabricated by particle impact) but also micropores with sizes of about 2 μm (created by sulfonation of PEEK) on the macroporous walls, and sulfonic acid (-SO3H) groups were introduced on PCPS surface. In addition, many n-MS nanoparticles were exposed on the microporous walls, which formed micro-nano structures. Moreover, the surface roughness and hydrophilicity of PCPS were obviously enhanced as compared with PC and PCP. Moreover, the apatite mineralization of PCPS in simulated body fluid (SBF) was obviously improved as compared with PC. Furthermore, compared with PC and PCP, PCPS exhibited antibacterial performances due to the presence of -SO3H groups. In addition, the responses (eg, adhesion and proliferation as well as differentiation) of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell of rat to PCPS were significantly promoted as compared with PC and PCP.
Conclusion: PCPS with macro-microporous surface containing -SO3H groups and micro-nano structures exhibited antibacterial activity and induced cell responses, which might possess large potential for bone substitute and repair.
Keywords: PEEK based composite, sulfonation, macro-microporous surface, antibacterial performances, cell responses