111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Lamin B1 在肺腺癌中过表达并通过 AKT 途径促进肺癌细胞的增殖
Authors Li W, Li X, Li X, Li M, Yang P, Wang X, Li L, Yang B
Received 5 September 2019
Accepted for publication 16 February 2020
Published 15 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3129—3139
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229997
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the biological effect and molecular mechanism of Lamin B1(LMNB1) in lung cancer cells and its significance for the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma(LUAD) patients.
Methods: In this study, Bioinformatics was performed to analyze the expression at mRNA level and prognosis effect of LMNB1 in LUAD from TCGA dataset. The immunohistochemistry(IHC) assay was conducted to analyzed the expression of LMNB1 at the protein level in LUAD tissues. The correlation between the expression of LMNB1 and the clinical factors in patients with LUAD was analyzed. Next, LMNB1 transfected into LUAD cell lines (A549 and PC-9) which was proved by Western blot. CCK8 assay, cloning formation assay, and xenograft assay were conducted to explore the effect and mechanism of LMNB1 on the proliferation of LUAD cell lines in vitro and in vivo.
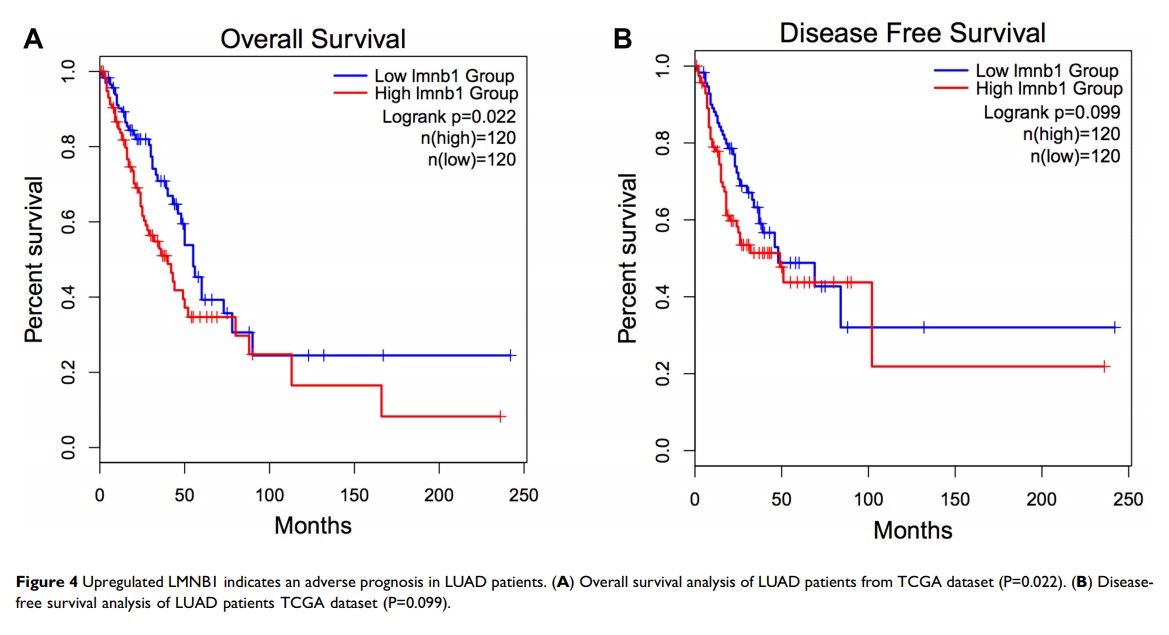
Results: The results of the present study demonstrated that LMNB1 was highly expressed in LUAD tissues and related to tumor stage. High LMNB1 expression was related with more advanced clinicopathological factors such as low degree of differentiation (P=0.02), large tumor size (P< 0.01), lymph node metastasis (P< 0.01) and higher tumor stage (P< 0.01). After knocking down LMNB1, the cell growth rate (P< 0.01) and the number of colonies (P< 0.01) were significantly reduced, and the level of the proliferating marker Ki67 (P< 0.01) was significantly decreased. At the same time, in vivo experiments showed that the tumor volume and tumor of the mice were significantly reduced (P< 0.01). Moreover, we found that knockdown LMNB1 can inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation by Western blot.
Conclusion: In summary, LMNB1 play an of vital roles in the growth of LUAD cells, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for the treatment of LUAD patients.
Keywords: lamin B1, lung adenocarcinoma, prognosis, malignant behavior