111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PFND1 通过激活 Wnt/β-Catenin 信号通路来预测胃癌的不良预后并促进细胞转移
Authors Zhou C, Guo Z, Xu L, Jiang H, Sun P, Zhu X, Mu X
Received 1 November 2019
Accepted for publication 23 March 2020
Published 16 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3177—3186
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S236929
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Prefoldin (PFDN) subunits have recently been found to function importantly in various tumor types, while the role of PFDN subunit 1 (PFDN1) in gastric cancer (GC) remains largely unknown. Herein, we aimed to investigate the clinical significance, the biological role and the underlying mechanism of PFDN1 in GC development.
Materials and Methods: PFDN1 expression levels were measured in human GC specimens by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), Western blot and immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, the effects of aberrant PFDN1 expression on GC cells behavior were assessed by wound-healing assay and transwell assay in vitro, and metastasis assay in nude mice, as well as Wnt/β-catenin signaling-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related markers by qRT-PCR and Western blot.
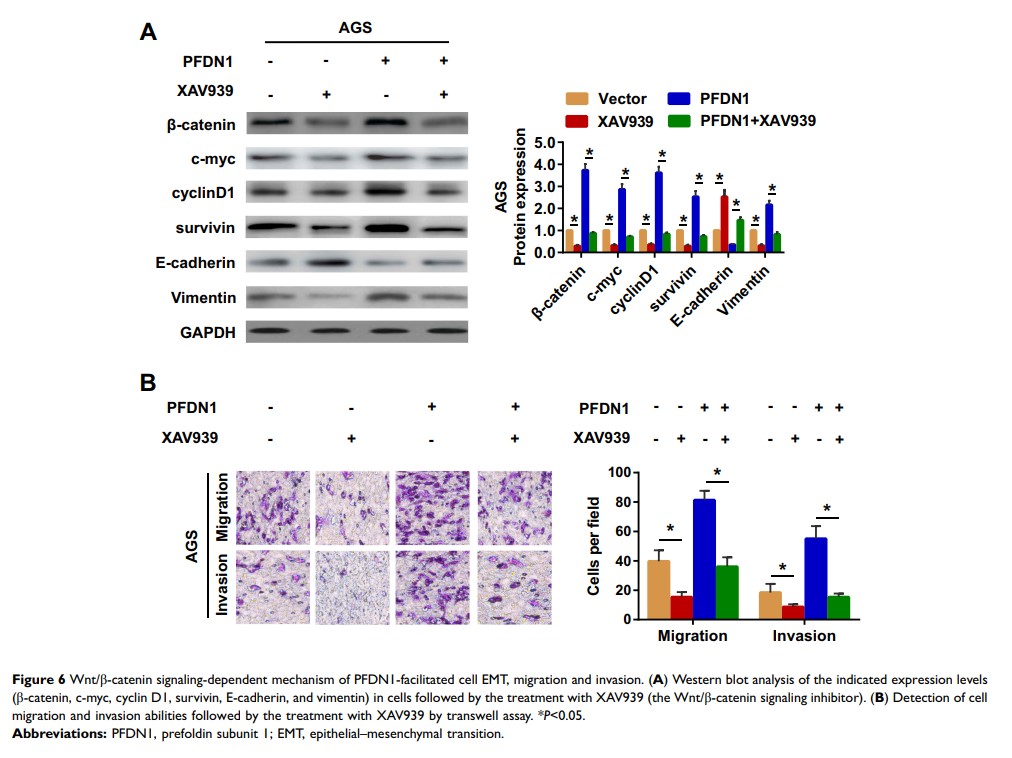
Results: PFDN1 levels were significantly upregulated in GC tissues compared with those in matched adjacent normal tissues. PFDN1 upregulation correlated strongly with clinical metastasis and unfavorable prognosis for GC patients. In vitro and in vivo studies revealed that PFDN1 facilitated GC cell migration, invasion and metastasis. Mechanically, PFDN1 modulated GC cell behavior by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-mediated EMT.
Conclusion: These results suggested a central role of PFDN1 in GC metastatic development via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, thus providing a potential therapeutic target for patients with GC.
Keywords: PFDN1, gastric cancer, epithelial–mesenchymal transition