111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

六磷酸肌醇酯和肌醇的组合通过 Wnt/β-Catenin 信号通路抑制小鼠结直肠癌的肝转移
Authors Liu X, Liu C, Chen C, Sun W, Ci Y, Li Q, Song Y
Received 30 January 2020
Accepted for publication 25 March 2020
Published 16 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3223—3235
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S247646
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Introduction: Colorectal cancer, one of the most common tumors, is mainly fatal because of the occurrence of liver metastasis. Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) and inositol (INS) were found, both, in vitro and in vivo to play an anti-tumor effect, whereas the combination of IP6 and INS was more effective than IP6 or INS alone.
Materials and Methods: The inhibitory effects of IP6, INS and the combination of IP6+INS on tumor progression and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer were investigated in an orthotopic transplantation model of colorectal cancer. The tumor-bearing mice were selected by in vivo bioluminescence imaging and were treated with IP6, INS, and IP6 combined with INS, respectively. All mice were sacrificed after 6 weeks of treatment. The cancer development and metastasis were compared among the groups. The expression of genes related to the Wnt/β-catenin in the model was analyzed.
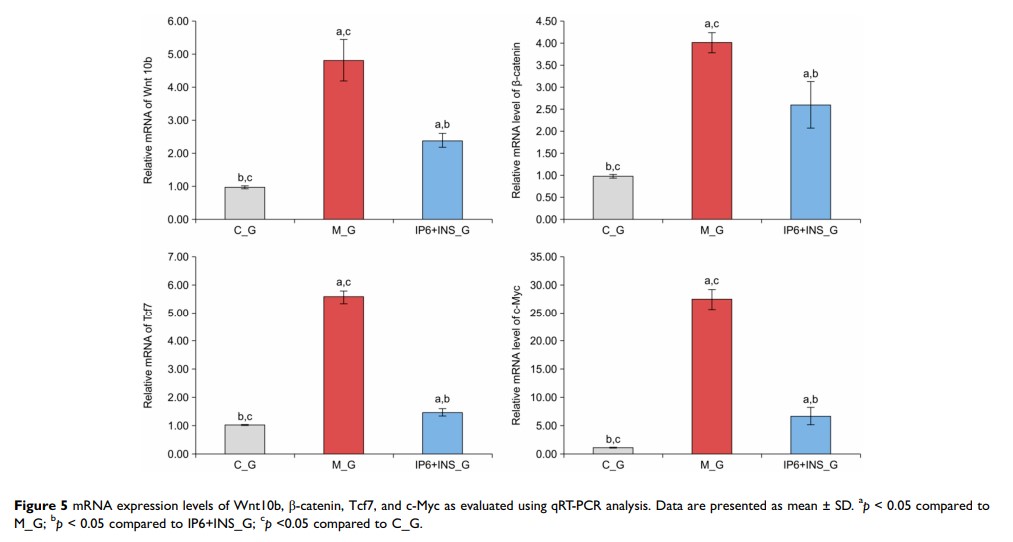
Results: The results demonstrated that liver metastasis was inhibited after treatment with IP6, INS, and IP6+INS. Compared to that of the M_G, survival period was extended, and tumor weight was lowered in IP6_G, INS_G, and IP6+INS_G. Besides, the liver metastatic area of mice in IP6+INS_G was relatively smaller than that in M_G, IP6_G, or INS_G. The results of RNA-seq analysis showed that the expressions of Wnt10b, Tcf7, and c-Myc were significantly downregulated in IP6+INS_G compared to that in M_G (P< 0.05). Results of real-time PCR and Western blot showed that mRNA and protein expressions of β-catenin, Wnt10b, Tcf7, and c-Myc were significantly lower in IP6+INS_G compared to that in M_G (P< 0.05).
Discussion: IP6+INS was more effective in inhibiting liver metastasis of colorectal cancer than IP6 or INS alone. The better inhibition effect may be accomplished through regulating the mutation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting Wnt10b, Tcf7, β-catenin, and c-Myc from abnormally high expression.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, liver metastasis, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, inositol hexaphosphate, inositol, mouse model