111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹酚酸通过抑制 P53 和 Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK 信号通路的周细胞凋亡来减轻自发性高血压大鼠的血脑屏障通透性
Authors Wu Q, Yuan X, Li B, Han R, Zhang H, Xiu R
Received 14 January 2020
Accepted for publication 15 March 2020
Published 16 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1523—1534
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S245959
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
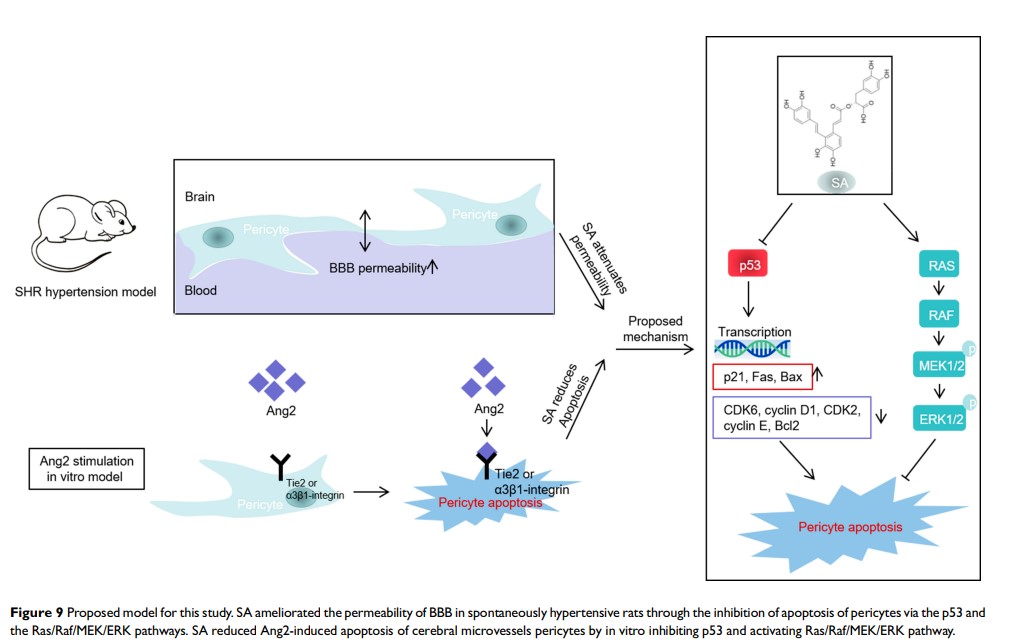
Objective: To investigate the effect of salvianolic acid A (SA) on the permeability of blood–brain barrier (BBB) and brain microvascular pericyte apoptosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR).
Methods: Evans Blue was used to determine the BBB permeability in control rats and SHR. Western blotting was used to evaluate the expression levels of relevant proteins in the pericytes isolated from the differentially treated animals. An in vitro model of hypertension was established by stimulating pericytes with angiopoietin-2 (Ang2). MTT assay was used to assess cell viability, and apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: SA attenuated BBB permeability in SHR in a dose-dependent manner. It downregulated pro-apoptotic proteins including p53, p21, Fas, FasL, cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3 and Bax in the pericytes of SHR and upregulated CDK6, cyclin D1, CDK2, cyclin E and Bcl2. In addition, SA activated the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in a dose-dependent manner by increasing the levels of Ras, Raf, p-MEK1, p-MEK2, p-ERK1 and p-ERK2. Finally, SA reduced Ang2-induced apoptosis of cerebral microvessels pericytes and decreased the proportion of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting the p53 pathway and activating the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Conclusion: SA reduced BBB permeability in spontaneously hypertensive rats, possibly by inhibiting Ang2-induced apoptosis of pericytes by activating the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: salvianolic acid A, blood–brain barrier, hypertension, pericytes, apoptosis