111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化锌纳米粒子可诱导人 iPSC 衍生的心肌细胞的线粒体生物合成障碍和心功能障碍
Authors Li Y, Li F, Zhang L, Zhang C, Peng H, Lan F, Peng S, Liu C, Guo J
Received 15 February 2020
Accepted for publication 1 April 2020
Published 21 April 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2669—2683
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S249912
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Shen
Background: Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) are one of the most widely used nanomaterials in a variety of fields such as industrial, pharmaceutical, and household applications. Increasing evidence suggests that ZnO NPs could elicit unignorable harmful effect to the cardiovascular system, but the potential deleterious effects to human cardiomyocytes remain to be elucidated. Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) have been increasingly used as a promising in vitro model of cardiomyocyte in various fields such as drug cardiac safety evaluation. Herein, the present study was designed to elucidate the cardiac adverse effects of ZnO NPs and explore the possible underlying mechanism using hiPSC-CMs.
Methods: ZnO NPs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. The cytotoxicity induced by ZnO NPs in hiPSC-CMs was evaluated by determination of cell viability and lactate dehydrogenase release. Cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial membrane potential were measured by high-content analysis (HCA). Mitochondrial biogenesis was assayed by detection of mtDNA copy number and PGC-1α pathway. Moreover, microelectrode array techniques were used to investigate cardiac electrophysiological alterations.
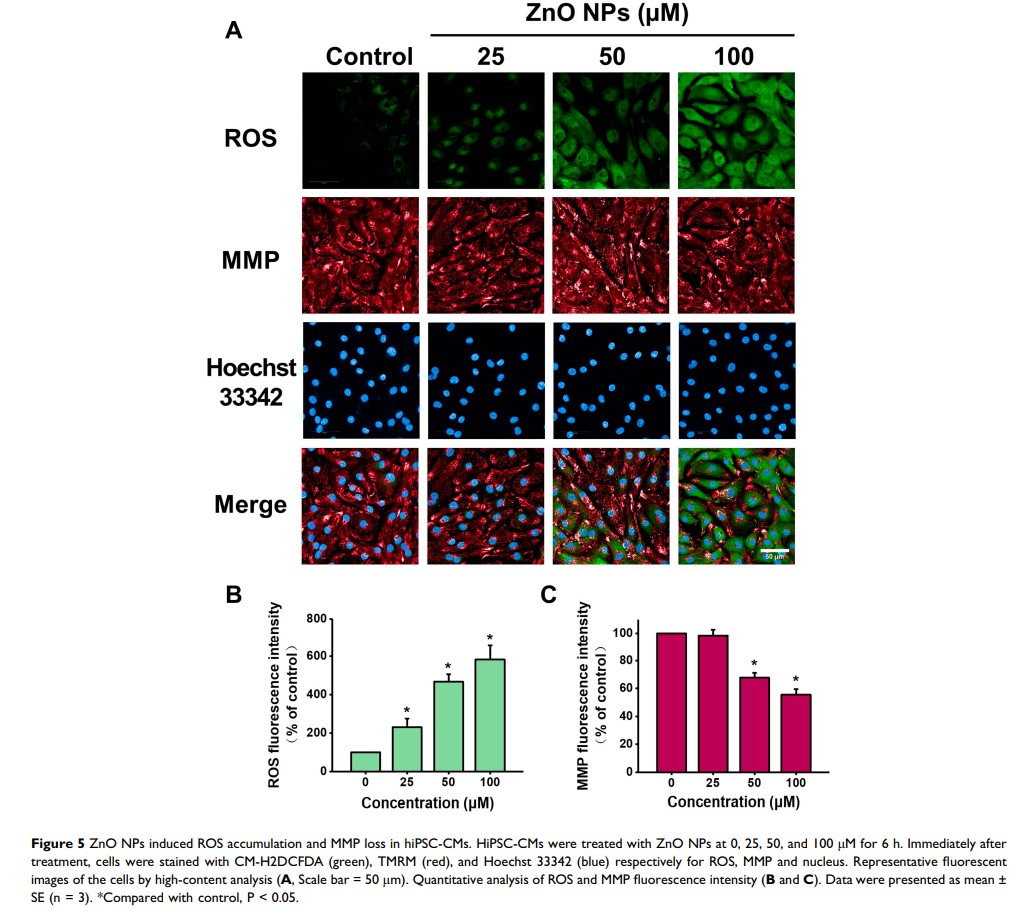
Results: We demonstrated that ZnO NPs concentration- and time-dependently elicited cytotoxicity in hiPSC-CMs. The results from HCA revealed that ZnO NPs exposure at low-cytotoxic concentrations significantly promoted ROS generation and induced mitochondrial dysfunction. We further demonstrated that ZnO NPs could impair mitochondrial biogenesis and inhibit PGC-1α pathway. In addition, ZnO NPs at insignificantly cytotoxic concentrations were found to trigger cardiac electrophysiological alterations as evidenced by decreases of beat rate and spike amplitude.
Conclusion: Our findings unveiled the potential harmful effects of ZnO NPs to human cardiomyocytes that involve mitochondrial biogenesis and the PGC-1α pathway that could affect cardiac electrophysiological function.
Keywords: Zinc oxide nanoparticles, ZnO NPs, human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived cardiomyocytes, hiPSC-CMs, cardiac dysfunction, mitochondrial biogenesis, PGC-1α