111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

没食子酸通过抑制依赖于 EGFR 的 CARM1-PELP1 复合物来阻止非小细胞肺癌的进展
Authors Wang D, Bao B
Received 21 August 2019
Accepted for publication 30 January 2020
Published 23 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1583—1592
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S228123
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common cause of cancer-related deaths. This study identified the regulatory pattern of gallic acid in NSCLC.
Methods: Human NSCLC cells were treated with different doses of gallic acid, after which, MTT assay and flow cytometry were performed to determine the survival and apoptotic rate of human NSCLC cells. Then, co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed to analyze the relationships between gallic acid, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and CARM1-PELP1. Next, we analyzed whether PELP1, CARM1 and EGFR were associated with the effects of gallic acid on NSCLC cells by conducting rescue experiments. The expression pattern of phosphorylated EGFR, EGFR, Ki67, as well as Fas, FasL and Caspase 3 proteins in cancer cells or xenografts was measured by Western blot analysis. Lastly, the role of gallic acid in the tumor growth was assessed in nude mice.
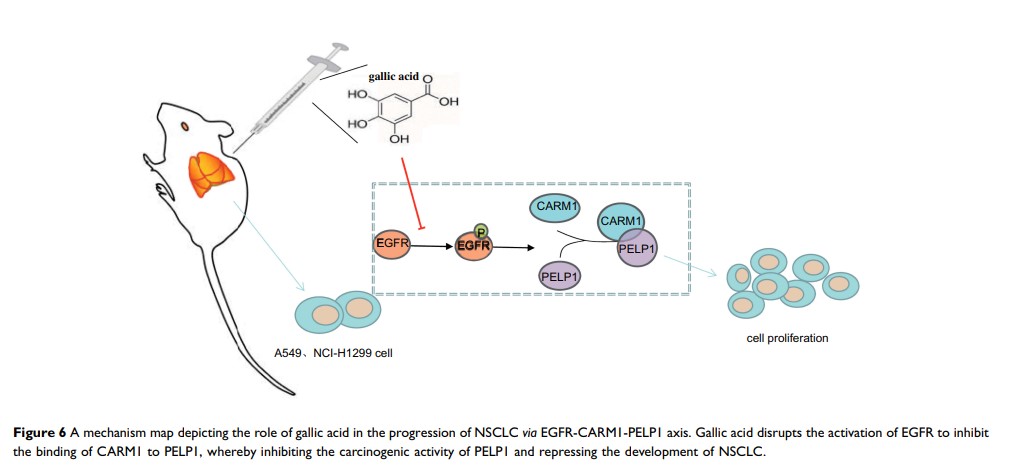
Results: The ideal dose of gallic acid that presented good suppressive effect on NSCLC cells were 30 μM, 50 μM and 75 μM, respectively. Gallic acid played an inhibiting role in the activation of EGFR, which further reduced the formation of CARM1-PELP1 complex, ultimately repressed the proliferation and elevated apoptosis of NSCLC cells. Meanwhile, CARM1 repression led to decreased growth, proliferation and migration abilities of NSCLC cells. Animal experiments confirmed that gallic acid contributed to the inhibition of tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: To sum up, gallic acid could potentially prevent NSCLC progression via inhibition of EGFR activation and impairment of the binding of CARM1 to PELP1, highlighting a novel therapy to dampen NSCLC progression.
Keywords: gallic acid, EGFR, CARM1, PELP1, non-small cell lung cancer, CARM1-PELP1 complex