111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

弥漫大 B 细胞淋巴瘤合并乙肝病毒感染患者的临床分析和预后意义
Authors Kang X, Bai L, Han C, Qi X
Received 31 December 2019
Accepted for publication 28 March 2020
Published 24 April 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2839—2851
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S244381
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: China is a high endemic area for the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The studies established the epidemiology between HBV and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but further research is necessary to clarify the potential link between HBV and DLBCL.
Patients and Methods: A total of 319 patients diagnosed with DLBCL were recruited as cases at First Medical Centre of Chinese PLA General Hospital from September 2010 to December 2018. During the same time, two age- and sex-matched controls were selected for each case, and the control groups comprised of 319 patients with non-hematological malignancy and 319 subjects with non-malignant conditions. Relative risk of developing DLBCL among individuals tested positive for hepatitis B surface antigen was calculated. After that, we retrospectively analyzed clinical data from DLBCL patients with different HBV infection statuses.
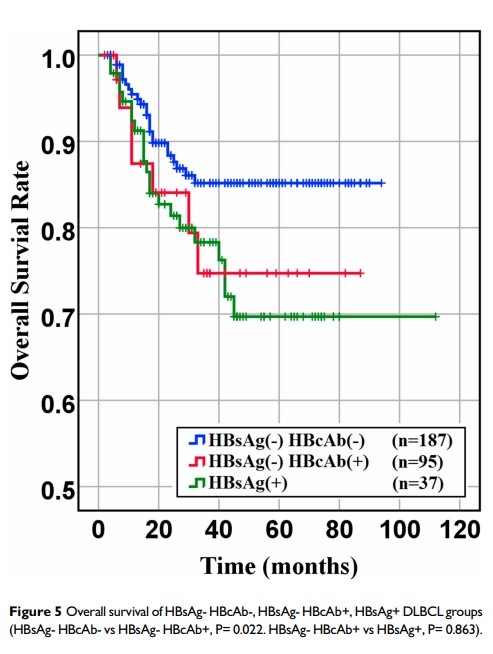
Results: The HBV infection rate of patients with DLBCL (11.60%) was significantly higher than the other two control groups (5.02% and 4.08%), indicating the risk of DLBCL may increased in HBV infections. Meanwhile, this study demonstrated an independent association between HBV infection and poorer clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that HBV infection may play an important role in the pathogenesis of DLBCL and show poor outcomes in HBV-endemic China.
Keywords: case–control study, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, hepatitis B viral