111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

实验鼠暴露于 ZnO 量子点后肝和肺的基因表达谱
Authors Yang Y, Li P, Lin Y, Li Z, Cui T, Song Z, Wu W, Lv S, Ji S
Received 20 January 2020
Accepted for publication 8 April 2020
Published 28 April 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2947—2955
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S246754
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: ZnO quantum dots (QDs) have drawn much attention recently as they are Cd-free, low-cost, and have excellent optical properties. With the expanded production and application of ZnO nanoparticles, concerns about their potential toxicity have also been raised.
Materials and Methods: We used RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to analyze the global gene expression of liver and lung tissues after ZnO QDs treatment. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened, with a fold change > 1.5 and padj < 0.05. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analyses were performed, and padj < 0.05 was considered significantly enriched. The RNA-seq results were validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
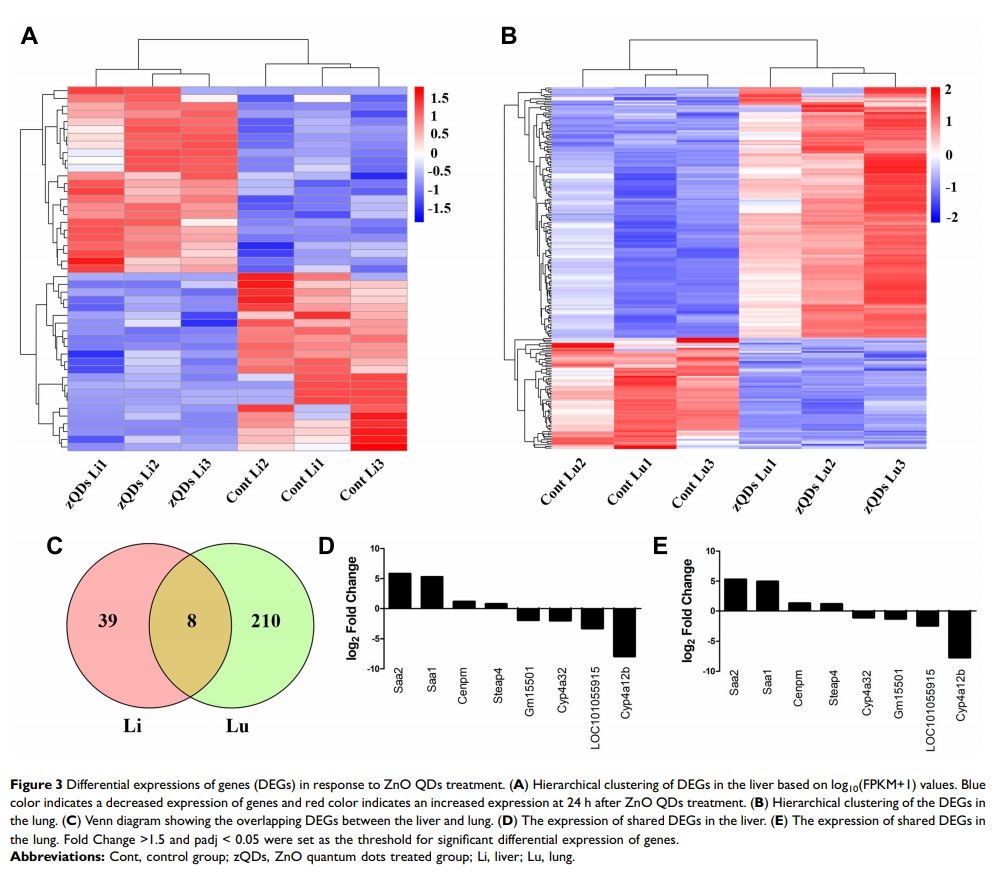
Results: A total of 47 and 218 genes were significantly differentially expressed in the liver and lung. Eight GO terms were enriched in the liver and lung, and retinol metabolism and the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway were shared in different tissues.
Discussion: According to DEGs and pathway enrichment analyses, inflammation might be induced in liver and lung tissues after intravenous injection of ZnO QDs. These findings will be helpful for future research and application of ZnO QDs.
Keywords: ZnO QDs, transcriptome, differentially expressed genes