111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

圣草酚通过 Akt/HIF-1α 信号通路对大鼠胶原诱导性关节炎的影响
Authors Lei Z, Ouyang L, Gong Y, Wang Z, Yu B
Received 22 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 29 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1633—1639
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S239662
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
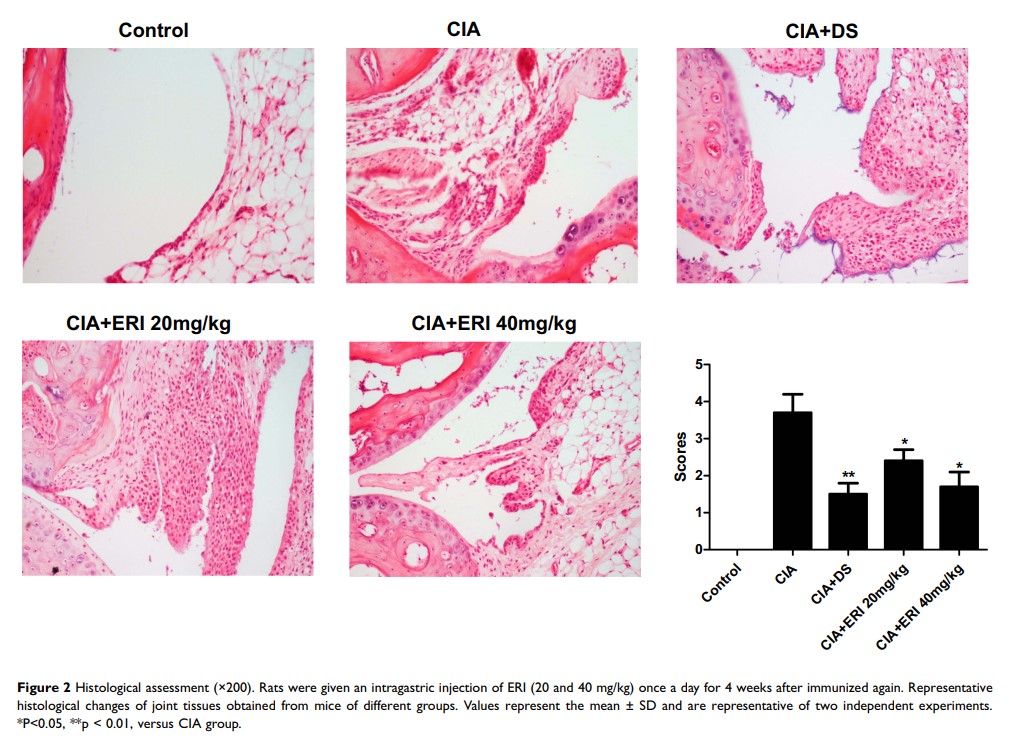
Purpose: The aim of the experiment was to explore the effect of eriodictyol (ERI) on arthritis.
Methods: We established a rat model of collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis (CIA) using type II collagen plus Freund’s complete adjuvant. We evaluated the degree of paw swelling, joint pathology, inflammatory cytokine levels, and the Akt/hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α signaling pathway in the CIA rats.
Results: ERI significantly ameliorated joint swelling; improved joint pathology; and suppressed the release of interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Moreover, ERI inhibited the Akt/HIF-1α pathway in the joints of rats and in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW264.7 cells.
Conclusion: ERI ameliorated arthritis in a manner involving the Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway.
Keywords: Eriodictyol, arthritis, inflammation, Akt/HIF-1α pathway