111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外来体通过激活自噬而改善大鼠脊髓损伤后的功能
Authors Gu J, Jin ZS, Wang CM, Yan XF, Mao YQ, Chen S
Received 6 November 2019
Accepted for publication 18 March 2020
Published 29 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1621—1631
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S237502
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Background: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a global medical problem. The smallest membrane-bound nanovesicles, known as exosomes, have a role in complex intercellular communication systems and can be used directly as therapeutic agents by acting as important paracrine factors. Nevertheless, the use of exosomes derived from BMSCs (BMSC-Exos) to treat SCI has been less, and the specific mechanism has not yet been reported.
Methods: BMSC-Exos were characterized by TEM, NTA and Western blot. The effects of BMSC-Exos treatment were compared by SCI in vivo model and a series of in vitro experiments.
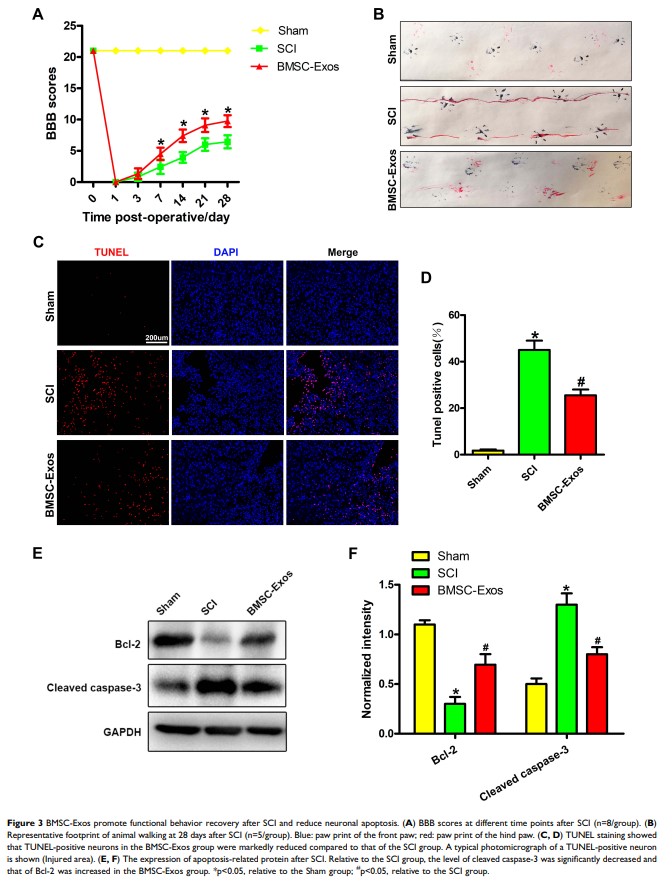
Results: BMSC-Exos were found to enhance the expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3IIB and Beclin-1 and enabled autophagosomes formation. After BMSC-Exos treatment, there was marked decline in the level of expression of proapoptotic protein cleaved caspase-3, while that of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was upregulated.
Conclusion: BMSC-Exos can attenuate neuronal apoptosis by promoting autophagy and promote the potential efficacy of functional behavior recovery in SCI rats. In summary, these findings expand the theoretical knowledge and forms a realistic route for the future treatment of SCI by BMSC-Exos.
Keywords: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes, spinal cord injury, apoptosis, autophagy