111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在间变性淋巴瘤激酶抑制剂影响下,基于药代动力学的药物相互作用:一个综述
Authors Zhao D, Chen J, Chu M, Long X, Wang J
Received 10 February 2020
Accepted for publication 2 April 2020
Published 30 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1663—1681
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S249098
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
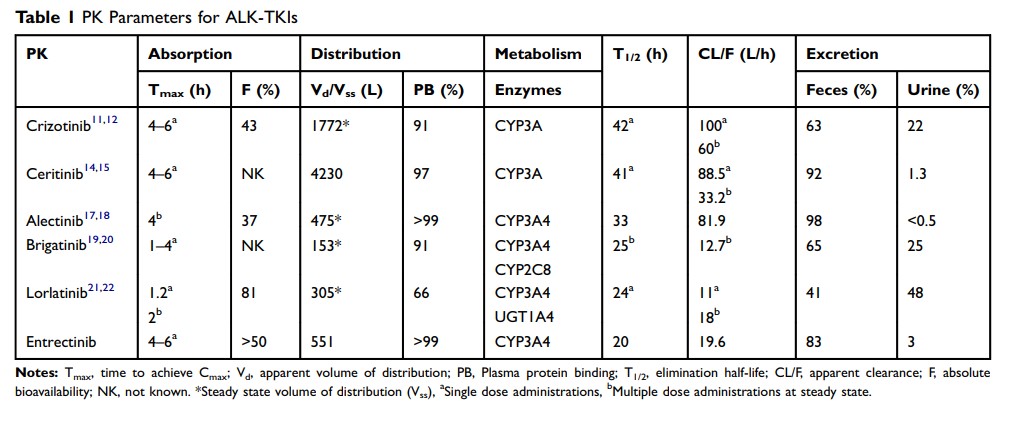
Abstract: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors are important treatment options for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), associated with ALK gene rearrangement. Patients with ALK gene rearrangement show sensitivity to and benefit clinically from treatment with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs). To date, crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, lorlatinib, and entrectinib have received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration and/or the European Medicines Agency for use during the treatment of ALK-gene-rearrangement forms of NSCLC. Although the oral route of administration is convenient and results in good compliance among patients, oral administration can be affected by many factors, such as food, intragastric pH, cytochrome P450 enzymes, transporters, and p-glycoprotein. These factors can result in increased risks for serious adverse events or can lead to reduced therapeutic effects of ALK-TKIs. This review characterizes and summarizes the pharmacokinetic parameters and drug–-drug interactions associated with ALK-TKIs to provide specific recommendations for oncologists and clinical pharmacists when prescribing ALK-TKIs.
Keywords: ALK, TKIs, NSCLC, PK, drug–drug interactions