111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

自发性糖尿病的 GK 大鼠胃部微生物群的特征:一项比较研究
Authors Kang X, Zhan L, Lu X, Song J, Zhong Y, Wang Y, Yang Y, Fan Z, Jiang X, Sun R
Received 25 January 2020
Accepted for publication 7 April 2020
Published 30 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1435—1447
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S242698
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Background: The Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat, developed from repeated inbreeding of glucose-intolerant Wistar rats, has been widely used to explore the development of spontaneous type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the gastric microbiota of GK and Wistar rats are still unclear. This study aimed to understand the gastric microbiota characteristics of GK rats by comparing it with non-diabetic Wistar rats.
Materials and Methods: Male Wistar rats and GK rats were housed in specific pathogen-free (SPF) environment for 12 weeks with free access to sterilized food and water. Body weight and random blood glucose (BG) levels were determined. At the end of the experiment, the gastric contents of the rats were collected for the identification of gastric microbiota using 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
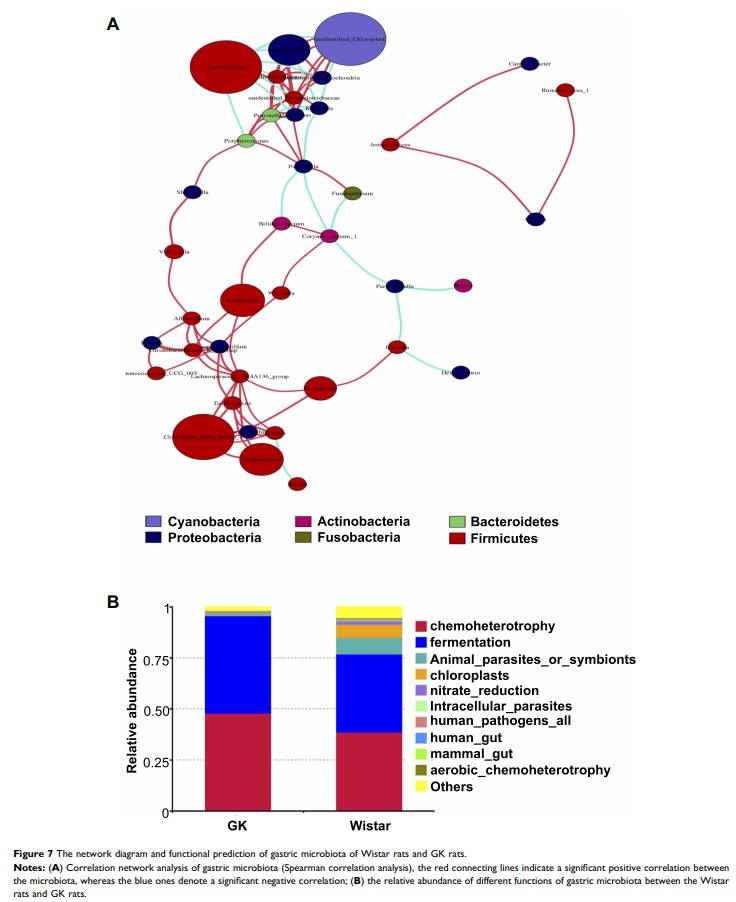
Results: The richness of gastric microbiota in GK rats was similar to that of Wistar rats (P > 0.05). The results of Shannon, Simpson, beta diversity indices, and ANOSIM analysis showed that alpha and beta diversity of gastric microbiota in GK rats were significantly lower than that of Wistar rats (P < 0.01). Firmicutes (96.0%), Proteobacteria (1.9%) and Cyanobacteria (0.8%) were the dominant gastric microbiota in GK rats accounting for 72.9%, 14.7% and 10.9%, respectively. Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) revealed that phylum Firmicutes and four genera (Anaerovibrio, Collinsella, Prevotellaceae _UCG_001 , and Lactobacillus ) were significantly abundant in the stomachs of GK rats. In contrast, seven genera (unidentified_Chloroplast, Porphyromonas, Neisseria, Rubrobacter, Veillonella, Lachnospiraceae_UCG_005 , and unidentified_Erysipelotrichaceae ) were significantly abundant in the stomachs of Wistar rats. Blood glucose was positively correlated with Anaerobibrio and Lactobacillus , and negatively correlated with four genera (Porphyromonas, Rubrobacter, Lachnospiraceae _UCG_005 , and unidentified_Erysipelotrichaceae ). In addition, chemoheterotrophy and fermentation were the most important functions of gastric microbiota.
Conclusion: The gastric microbiota of GK rats with spontaneous T2DM showed the typical characteristics of low diversity and significant enrichment of Firmicutes phylum and four genera (Anaerovibrio, Collinsella, Prevotellaceae _UCG_001 , and Lactobacillus ) compared with gastric microbiota of Wistar rats.
Keywords: gastric microbiota, type-2 diabetes mellitus, GK rat, wistar rat, 16S rRNA gene sequencing