111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过提升骨髓增生异常综合症中 DNA 甲基转移酶的表达,二硫化砷可促进低甲基化
Authors Zhou QB, Liu ZT, Wang HZ, Guo XQ, Xu YG, Hu XM
Received 25 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 March 2020
Published 30 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1641—1650
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S239158
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
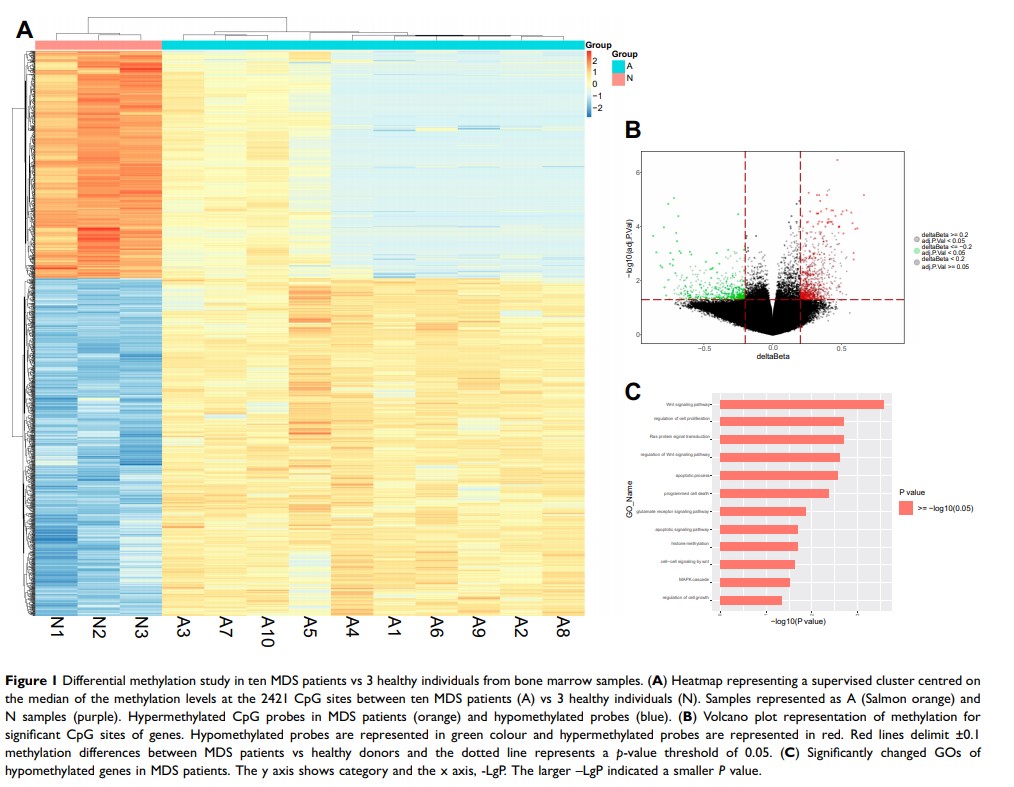
Background: Previous studies have shown that DNA methylation plays a significant role in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In addition to hypermethylation, aberrant hypomethylation can result in the transcriptional activation of oncogenes in cancer, including MDS. Therefore, drugs targeting DNA hypomethylation are needed for the treatment of MDS. This study aimed to investigate whether As2S2 promoted hypomethylation by increasing DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) expression in MDS.
Patients and Methods: Ten bone marrow samples from MDS patients and 3 healthy donors were obtained for the examination of the DNA methylation with a Human Methylation 850K BeadChip. The mRNA expressions for the DNMTs in the ten MDS patients and 3 controls were compared by Q-PCR. Then, the MDS cell line SKM-1 was treated with As2S2. After 2 days of treatment, Human Methylation 850K BeadChip was applied to analyze the changes of gene methylation status in the cells. Q-PCR and Western blot were taken to test the changes of mRNA and protein expressions for DNMTs in SKM-1 cells after treatment.
Results: Five hundred ninety-two abnormally hypomethylated genes were found in MDS patients compared to those in controls by Human Methylation 850K. The mRNA expressions of DNMTs (DNMT1, DNMT3a and DNMT3b) in MDS patients were significantly lower than those in healthy individuals. The IC50 value of As2S2 for SKM-1 cells was 4.97 μmol/L.Treatment with As2S2 at 2 μmoL/L resulted in significant alterations in the methylation levels at 1718 sites in SKM-1 cells compared to those in the controls. Hypermethylation was observed in 1625 sites (94.58%), corresponding to 975 genes, compared to those in the controls. Finally, the expression levels of DNMTs (DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b) significantly increased in SKM-1 cells treated with As2S2 at 2 μmoL/L and 4 μmoL/L.
Conclusion: These data show a potential clinical application of As2S2 as an innovative hypermethylation agent in MDS.
Keywords: arsenic disulfide, myelodysplastic syndrome, hypermethylation, SKM-1 cell line