110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

腹腔镜袖胃切除术后血清 Nesfatin-1 水平的变化与非酒精性脂肪肝疾病的改善相关
Authors Yang K, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Chen F, Shen M, Wang Y
Received 16 January 2020
Accepted for publication 15 March 2020
Published 1 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1459—1464
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S246281
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a serious and widespread disease worldwide. Bariatric surgery is one of the treatments for NAFLD. Nesfatin-1 is located in the brain, periphery and plasma. We studied the relationship between nesfatin-1 changes after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) and NAFLD remission.
Methods: A total of 29 patients participated in the study, which collected clinical information on the patients and indicators of liver function, hepatic steatosis score and nesfatin-1 level before and after LSG.
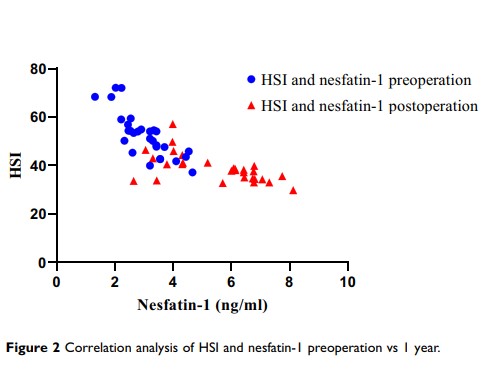
Results: The average BMI of the patients before surgery was 42.63± 8.91 kg/m2, and the average BMI was 28.54± 5.63 kg/m2 one year after surgery (p < 0.05). One year after LSG, the total weight loss percentage (TWL%) was 32.11± 7.10%. The mean value of nesfatin-1 before surgery was 3.04± 0.81 ng/mL, and the mean value of nesfatin-1 was 5.52± 1.55 ng/mL at one year after surgery (p < 0.05). The average preoperative hepatic steatosis index (HSI) score of the patients was 52.55± 9.17, and the average postoperative HSI score was 38.84± 5.82 (p < 0.05). Before LSG (p < 0.05, r= − 0.81) and 1 year after surgery (p < 0.05, r = − 0.58), HSI and nesfatin-1 were significantly negatively correlated. Percentage of increased nesfatin-1 and percentage of decreased HSI showed positive correlation after LSG.
Conclusion: There was a negative correlation between HSI and nesfatin-1 before and after LSG, which may suggest that nesfatin-1 plays a role in NAFLD.
Keywords: nesfatin-1, NAFLD, bariatric surgery, LSG