110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SCAMP3 促进神经胶质瘤增殖并通过多种信号通路指示不良预后
Authors Li C, Zhang Z, Lv P, Zhan Y, Zhong Q
Received 15 December 2019
Accepted for publication 6 April 2020
Published 1 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3677—3687
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S242462
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
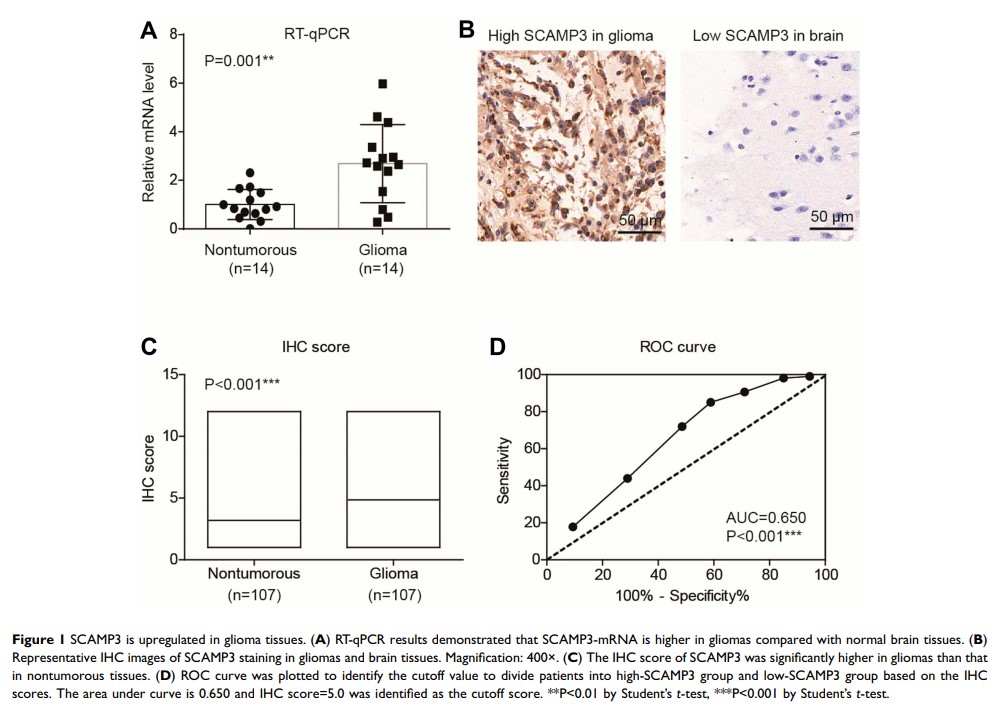
Introduction: The secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 3 (SCAMP3) is a component of post-Golgi membranes, functions as a protein carrier and is critical for subcellular protein transportation. Limited studies revealed an elevated expression of SCAMP3 in breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma; however, its role in glioma remains unknown. The aim of our study is to investigate the expression pattern and functional mechanisms of SCAMP3 in glioma.
Methods: mRNA and protein levels of SCAMP3 were examined in glioma tissues together with nontumorous brain tissues by using quantitative real-time-PCR and immunohistochemistry staining. The prognostic role of SCAMP3 in glioma was evaluated through univariate and multivariate analyses. In vitro and in vivo assays were conducted to explore the underlying mechanisms of SCAMP3-induced glioma progression.
Results: The expression level of SCAMP3 was higher in glioma tissues than that in normal brain tissues. High protein level of SCAMP3 was correlated with larger tumor size and advanced WHO grade. Glioma patients with high-SCAMP3 level had worse overall survival. In addition, SCAMP3 was defined as an independent risk factor of glioma prognosis. Cellular and xenograft studies revealed that SCAMP3 promotes glioma proliferation possibly through enhancing EGFR and mTORC1 signaling.
Discussion: Our studies revealed that high-SCAMP3 expression level was closely related to the unfavorable clinical features and poor prognosis of glioma patients. SCAMP3 may serve as an invaluable prognostic indicator and novel therapeutic target for glioma treatment.
Keywords: glioma, SCAMP3, proliferation, prognosis, EGFR