110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-575 的下调通过靶向 p27 Kip1 抑制胆囊癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Qin Y, Mi W, Huang C, Li J, Zhang Y, Fu Y
Received 2 September 2019
Accepted for publication 18 February 2020
Published 1 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3667—3676
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229614
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Background: Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is the most common biliary tract malignant cancer worldwide. It has been reported that microRNA-575 (miR-575) was involved in the tumorigenesis of many cancers. However, the role of miR-575 during the progression of GBC remains largely unknown.
Methods: The expression of miR-575 in GBC cells was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The proliferation of GBC cells was examined by CCK-8 assay and Ki-67 staining. Apoptosis of GBC cells was measured by flow cytometry, and cell invasion was tested by transwell assay. Moreover, protein expressions in GBC cells were evaluated using Western blot. The target gene of miR-575 was predicted using Targetscan and miRDB. Finally, xenograft tumor model was established to verify the function of miR-575 in GBC in vivo.
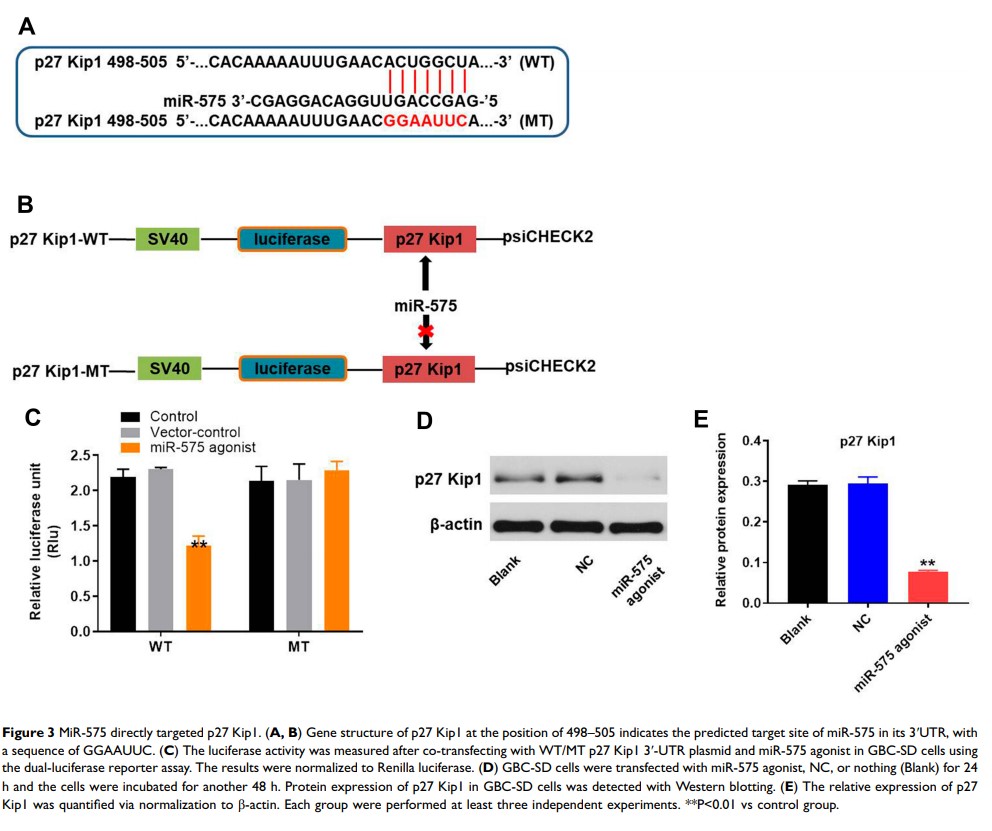
Results: Our findings indicated that miR-575 antagonist decreased the proliferation and invasion of GBC cells. In addition, miR-575 antagonist significantly induced apoptosis of GBC cells via inducing G1 arrest. Meanwhile, p27 Kip1 was found to be a direct target of miR-575 with luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, miR-575 antagonist significantly decreased the expressions of CDK1 and cyclin E1 and upregulated the levels of cleaved caspase3 and p27 Kip1 in GBC cells. Finally, miR-575 antagonist notably suppressed GBC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Downregulation of miR-575 significantly inhibited the tumorigenesis of GBC via targeting p27 Kip1. Thus, miR-575 might be a potential novel target for the treatment of GBC.
Keywords: miR-575, p27 Kip1, gallbladder cancer