110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

格列美脲-二甲双胍加合物的抗乳腺癌作用及其机制
Authors Long L, Hu X, Li X, Zhou D, Shi Y, Wang L, Zeng H, Yu X, Zhou W
Received 27 November 2019
Accepted for publication 2 April 2020
Published 4 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3777—3788
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240252
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Compound adduct is a eutectic crystal formed by non-covalent bonds of two compounds or multiple compounds with water. Emerging evidence suggests that adduct could be different from the simple physical mixture of the individual compounds and has some new features. Recent studies reported that both glimepiride (Gli) and metformin (Met) may possess an anti-breast cancer effect besides anti-diabetic effect. In the current study, we synthesized glimepiride-metformin adduct (GMA) and examined its anti-breast cancer effect in vitro and in vivo to explore its potential in treatment of breast cancer in diabetic patients.
Methods: GMA was synthesized from Gli, Met and water at a molar molecular mass of 1:1:1 and identified by infrared spectroscopy. MTT assay, colony formation assay and wound healing assay were performed to examine the effects of GMA on cell viability and migration of human breast cancer cell lines CAL-148, MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-231and MCF-7. The effect of GMA on cell cycle and apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry. The orthotopic implantation model was established to observe the inhibitory effect of GMA on tumor growth. The expression of Ki67 was detected by immunohistochemistry. RT-qPCR and Western blotting were performed to investigate mechanisms for the function of GMA.
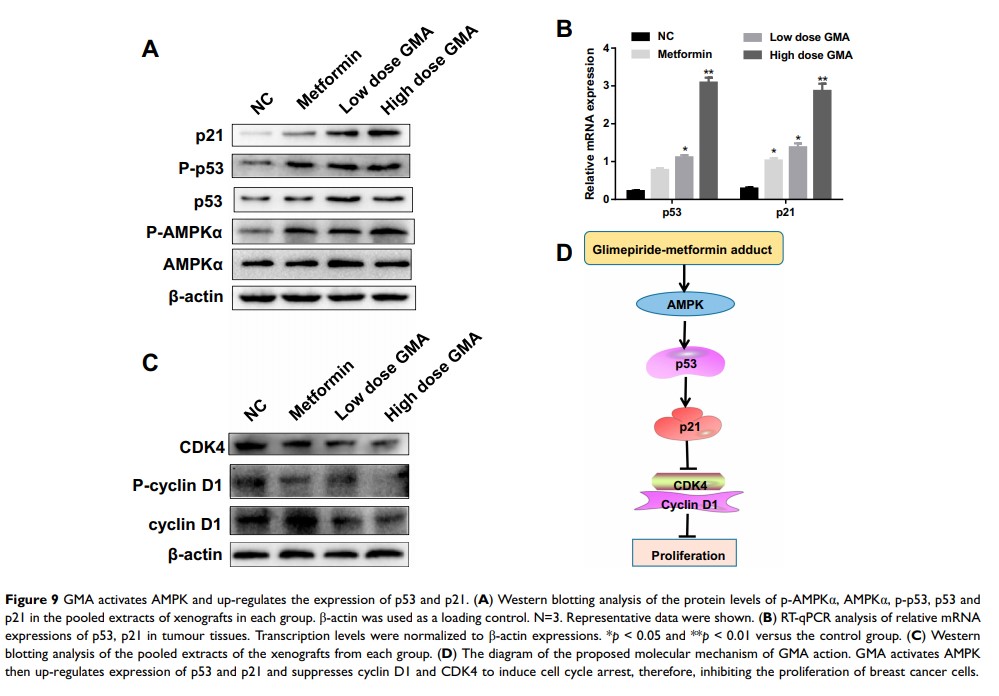
Results: Both MTT and colony formation assays showed that GMA inhibited breast cancer cell viability, and the effect was greater than Gli alone, Met alone and the combination. In vivo study showed that GMA had an inhibitory effect on tumor growth of CAL-148 xenografts. Flow cytometry analysis indicated that GMA induced G1/S phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. RT-qPCR and Western blotting analyses showed that GMA activated AMPK, and up-regulated expression of p53 and p21, and down-regulated expression of cyclin D1 and CDK4.
Conclusion: GMA suppresses cell viability of breast cancer cells, and its effect is greater than Gli and Met alone or combination at the same concentration. GMA inhibits breast cancer cell growth in vivo. The antitumor effect of GMA may be related to the activation of AMPK resulting in up-regulation of p53 and p21 and down-regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4.
Keywords: glimepiride, metformin, adduct, breast cancer, cell cycle, AMPK