110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

带状疱疹后神经痛的大脑在疼痛缓解前和疼痛缓解后六个月的功能和结构变化
Authors Zhang Y, Cao S, Yuan J, Song G, Yu T, Liang X
Received 21 January 2020
Accepted for publication 17 April 2020
Published 4 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 909—918
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S246745
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr E Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Objective: Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to detect whether 6 months after pain relieving, the structural and functional abnormalities in the brain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) patients are changeable.
Methods: Fifteen successfully treated PHN patients were enrolled; the brain activity and structural abnormalities were detected and compared before and 6 months after treatment. The functional parameters were evaluated with resting-state functional MRI technique, i.e., the regional homogeneity (ReHo) and fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF). Structural changes were detected with voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI).
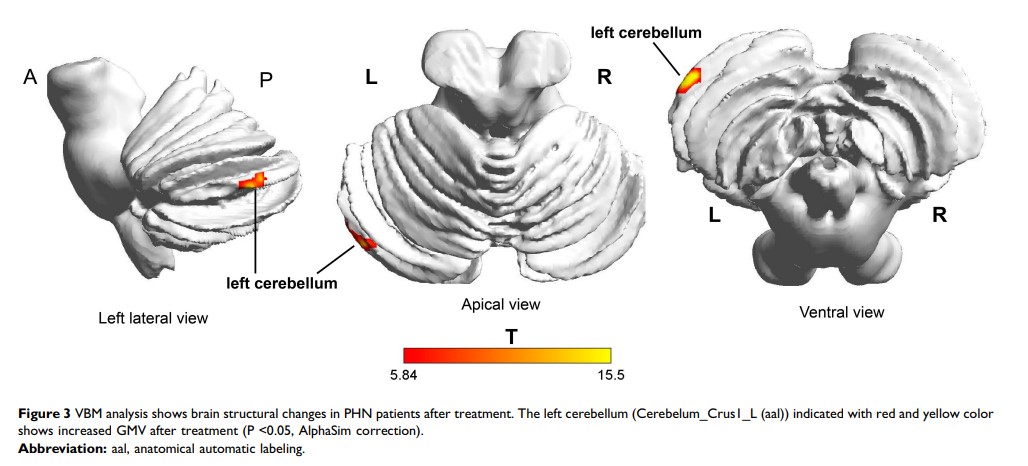
Results: Six months after pain relieving, PHN brain showed different ReHo and fALFF values in the frontal lobe, caudate, supramarginal gyrus, anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), cuneus, middle temporal gyrus, and cerebellum. In addition, VBM intensity in the cerebellum increased; DKI values decreased in the thalamus and increased in the temporal lobe after successful treatment.
Conclusion: Six months after pain relieving, functional and structural changes exist in PHN brain. Changes in some differential areas in PHN brain, such as ACC, frontal lobe, thalamus, and temporal lobe indicate that the central plasticity may be reversible after chronic pain relieving.
Keywords: postherpetic neuralgia, PHN, functional magnetic resonance imaging, regional homogeneity, ReHo, fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, fALFF