110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹酚酸 A 通过抑制 NF-κB 和 p38/MAPK 信号通路表现出抗炎和抗关节炎作用
Authors Feng S, Cong H, Ji L
Received 24 October 2019
Accepted for publication 12 February 2020
Published 8 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1771—1778
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S235857
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA), a chronic joint disease, combines with massive inflammation and plays a vital role in cartilage degeneration. The main strategy in clinic is controlling inflammation, thereby treating osteoarthritis. Salvianolic acid A (SAA) is a type of phenolic acid, derived from a traditional chinese herbal medicine Danshen that is extensively used clinically.
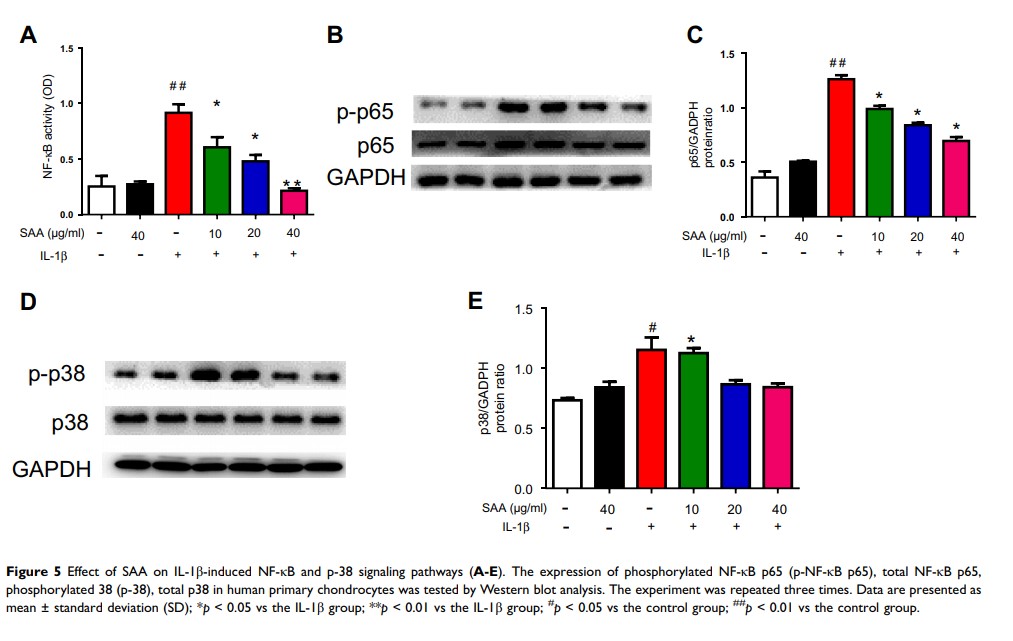
Methods and Results: We observed the anti-inflammatory and antiarthritic effects of SAA in IL-1β-stimulated cells. We found that SAA evidently decreased the expression of mainly inflammatory factors, exerted the remarkable effects of anti-inflammation and anti-arthritis. Furthermore, SAA inhibited the expression of Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP1, MMP13), and ADAMTS-5 and raised the synthesis of collagen II and aggrecan. Additionally, the results indicated that SAA gave rise to the effects by down-regulation of NF-κB and p38/MAPK pathways.
Discussion: Our study demonstrates that SAA may be a promising anti-inflammatory for the treatment of OA in clinic.
Keywords: Salvianolic acid A, Osteoarthritis, MMPs, NF-κB pathway