110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

新型 mTOR 抑制剂用于肝细胞癌放射增敏的虚拟筛选和优化
Authors Feng YQ, Gu SX, Chen YS, Gao XD, Ren YX, Chen JC, Lu YY, Zhang H, Cao S
Received 13 February 2020
Accepted for publication 9 April 2020
Published 8 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1779—1798
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S249156
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Radiotherapy has an ameliorative effect on a wide variety of tumors, but hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is insensitive to this treatment. Overactivated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) plays an important part in the resistance of HCC to radiotherapy; thus, mTOR inhibitors have potential as novel radiosensitizers to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy for HCC.
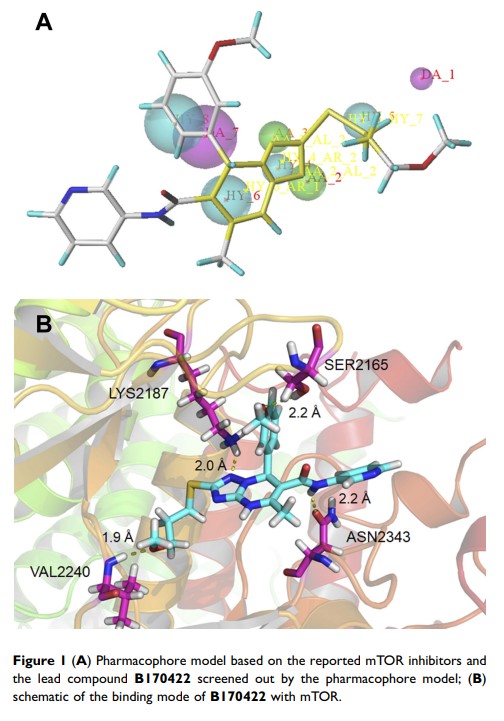
Methods: A lead compound was found based on pharmacophore modeling and molecular docking, and optimized according to the differences between the ATP-binding pockets of mTOR and PI3K. The radiosensitizing effect of the optimized compound ( 2a) was confirmed by colony formation assays and DNA double-strand break assays in vitro. The discovery and preclinical characteristics of this compound are described.
Results: The key amino acid residues in mTOR were identified, and a precise virtual screening model was constructed. Compound 2a, with a 4,7-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold, exhibited promising potency against mTOR (mTOR IC50=7.1 nmol/L (nM)) with 126-fold selectivity over PI3Kα. Moreover, 2a significantly enhanced the sensitivity of HCC to radiotherapy in vitro in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: A new class of selective mTOR inhibitors was developed and their radiosensitization effects were confirmed. This study also provides a basis for developing mTOR-specific inhibitors for use as radiosensitizers for HCC radiotherapy.
Keywords: virtual docking, HCC, kinase inhibitor, mTOR, radiosensitizer