110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

达妥昔单抗可通过穿孔素-粒酶 B 途径协同增强自然杀伤细胞对视网膜母细胞瘤的细胞毒性作用
Authors Wang H, Yang J, Pan H, Tai MC, Maher MH, Jia R, Ge S, Lu L
Received 24 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 April 2020
Published 8 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3903—3920
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S228532
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Conventional chemotherapy and enucleation usually fail to cure advanced retinoblastoma. We investigated the retinoblastoma immune microenvironment and the efficacy of the combination of dinutuximab and CD16-expressing NK-92MI (NK-92MIhCD16-GFP) cells on retinoblastoma cells in this study.
Patients and Methods: Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry (FC) were performed to assess the expression level of GD2 in retinoblastoma tissues and cells. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), immunohistochemisrztry and immunocytochemistry were conducted to assess the retinoblastoma immune microenvironment and the integrity of the blood-retinal barrier (BRB). After overexpressing CD16 in NK-92MI cells, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) was applied to select the positive subpopulation. LDH assays and FC were used to detect LDH release and apoptosis in retinoblastoma cells subjected to a combination of dinutuximab and NK-92MIhCD16-GFP cells. Finally, the release of perforin-granzyme B and the expression of CD107a in NK-92MIhCD16-GFP stimulated by retinoblastoma cells were assessed via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and FC in the presence of dinutuximab or an isotype control.
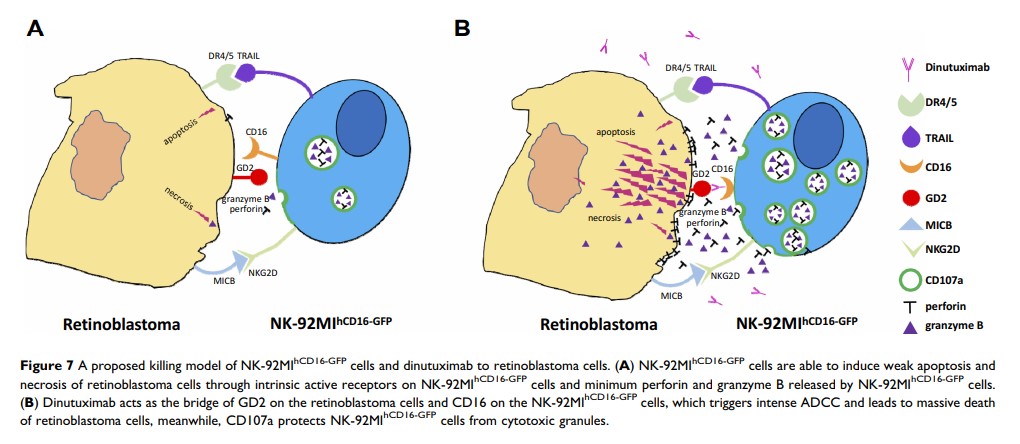
Results: GD2 was heterogeneously expressed in retinoblastoma tissues and cell lines and positively correlated with proliferation and staging. GSEA revealed the immunosuppressive status of retinoblastoma microenvironment. The immune cell profile of retinoblastoma tissues and vitreous bodies suggested BRB destruction. LDH release and apoptosis in retinoblastoma cells caused by NK-92MIhCD16-GFP cells were significantly enhanced by dinutuximab. Finally, the release of perforin-granzyme B and the expression of CD107a in NK-92MIhCD16-GFP cells stimulated by retinoblastoma cells were obviously increased by dinutuximab.
Conclusion: This study indicates that retinoblastoma impairs the integrity of the BRB and contributes to dysregulated immune cell infiltrates. GD2 is a specific target for natural killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapy and that the combination of dinutuximab and NK-92MIhCD16-GFP cells exerts potent antitumor effects through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
Keywords: tumor immune microenvironment, natural killer cells, NK-92MI, GD2, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity