110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国辽宁省奶牛乳腺炎金黄色葡萄球菌分离株的体外抗生素敏感性、毒力基因分布和生物膜产生
Authors Zhang DX, Li Y, Yang XQ, Su HY, Wang Q, Zhang ZH, Liu YC, Tian CL, Cui CC, Liu MC
Received 30 January 2020
Accepted for publication 16 April 2020
Published 11 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1365—1375
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S247765
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sahil Khanna
Purpose: The aim of this study was to identify the subtype, characterize the antimicrobial resistance, determine the virulence gene distribution, and analyze the biofilm production of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis milk samples in the Liaoning Province of China.
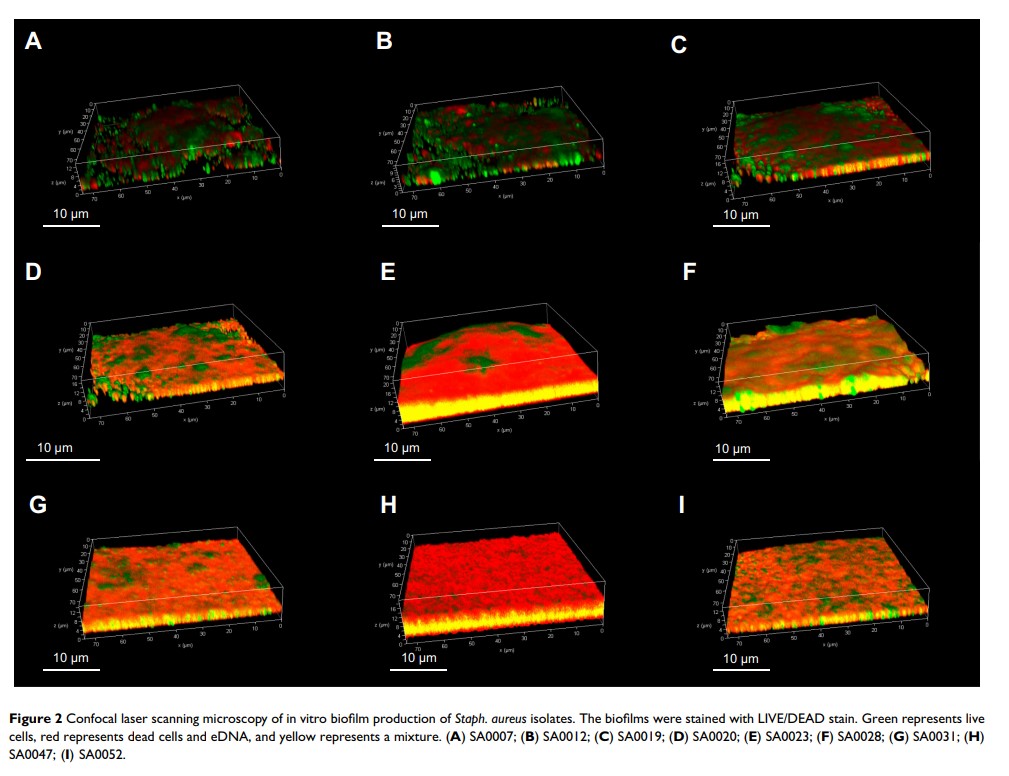
Materials and Methods: In total, 56 Staph. aureus isolates were collected and identified in this study; the isolates were divided into different spa types based on the sequence of the polymorphic X region of the spa gene. Additionally, antimicrobial susceptibility was investigated using the broth microdilution method, and 18 virulence genes were detected using PCR. Biofilm formation was measured by spectrophotometry with crystal violet staining and observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Results: There were 12.12% (56/462) milk samples that were positive for Staph. aureus . These isolates were nonsusceptible to sulfamethoxazole (100%), penicillin (76.9%), daptomycin (76.79%), clindamycin (69.64%), and oxacillin (60.71%); however, the majority of the isolates (80.4%) were susceptible to amoxicillin/clavulanate. The predominant virulence genes encoded the cytotoxins, hla (94.64%) and hlb (89.29%), and the adhesion factors clfA (89.29%), clfB (89.29%), and fnbB (80.36%). Comparatively, virulence genes related to other adhesion factors such as cna (8.93%) and enterotoxins, such as seg (26.79%), sea (16.07%), seb (7.14%), and sec (7.14%) were detected at relatively lower rates. The following eight spa types were identified: t267 (35.84%), t730 (22.64%), t518 (15.09%), t1190 (11.32%), t1456 (9.43%), t224 (1.88%), t9129 (1.88%), and t177 (1.88%). The highest biofilm production was observed for t267. Staph. aureus exhibited various patterns of biofilm formation, with the biofilm often being associated with a tower-shaped structure or a thicker biofilm.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that Staph. aureus isolates from dairy cows with mastitis in the Liaoning Province of China were non-susceptible to sulfamethoxazole, penicillin, daptomycin, oxacillin, and clindamycin. Additionally, the most prevalent subtype was t267, which displayed resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents and harbored several virulence genes, including clfA, clfB, fnbB, hla , and hlb .
Keywords: Staph. aureus , antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors, biofilm formation, mastitic dairy