110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA MALAT1 通过 PI3K/AKT/m-TOR 信号通路促进口腔鳞状细胞癌的 EMT 过程和顺铂耐药性
Authors Wang R, Lu X, Yu R
Received 27 February 2020
Accepted for publication 22 April 2020
Published 12 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4049—4061
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S251518
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Background: Cisplatin (DDP) is the first-line chemotherapy agent for the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The emergence of DDP resistance leads to diminished drug efficacy and survival benefit. lncRNA MALAT1 has been considered as one of the most important factors in OSCC. It has also been reported to enhance chemo-resistance in other kinds of carcinomas. However, little is known about the role of lncRNA MALAT1 in DDP resistance of OSCC.
Materials and Methods: Two kinds of human DDP-resistant cell lines (CAL-27R and SCC-9R) were developed from cisplatin-naïve cell lines (CAL-27 and SCC-9, respectively) as in vitro cell models. Cell transfection was performed to overexpress or knockdown MALAT1 in these cells. Mouse xenograft models were also established. The following measurements were performed: cell proliferation, colony formation, wound healing, transwell, and TUNEL assays, as well as Western blot and immunofluorescence staining.
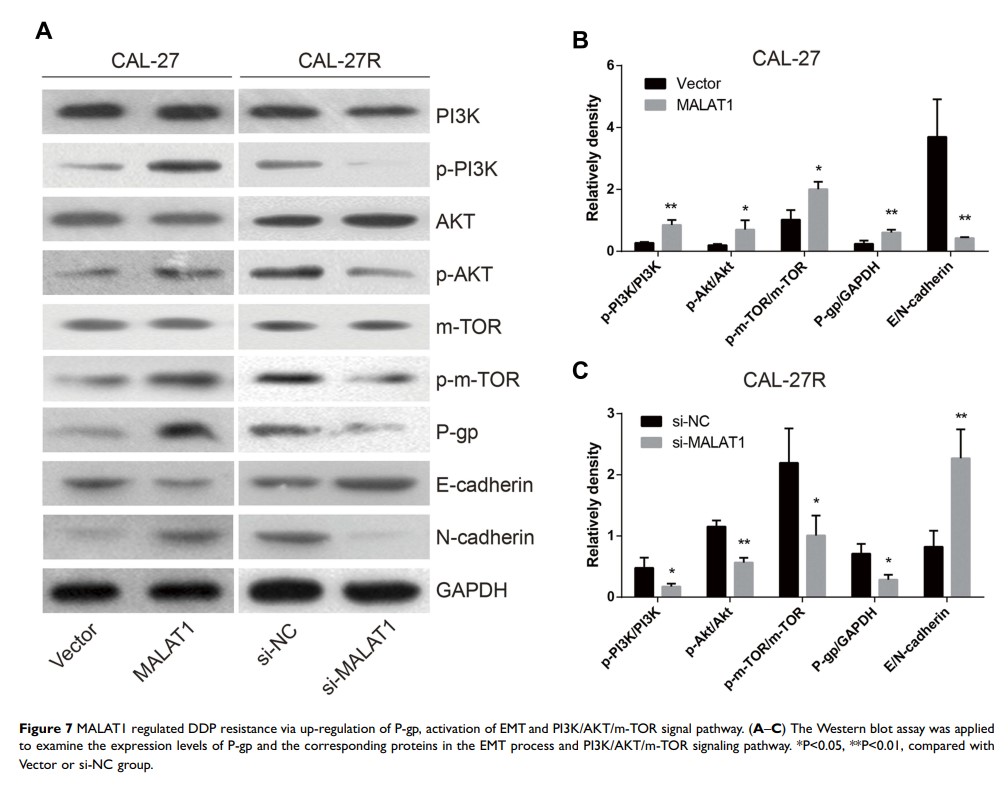
Results: DDP-resistant cells showed higher expression level of MALAT1 compared to cisplatin-naïve cells. The overexpression of MALAT1 in cisplatin-naïve cells enhanced DDP resistance and suppressed apoptosis in OSCC cells. However, the knockdown of MALAT1 in DDP-resistance cells induced apoptotic cell death and restored the sensitivity to DDP. Further analyses suggested that MALAT1 might promote DDP resistance via regulating P-glycoprotein expression, epithelial–mesenchymal transition process, and the activation of PI3K/AKT/m-TOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: MALAT1 might be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of DDP-resistant OSCC.
Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma, cisplatin resistance, lncRNA MALAT1, P-glycoprotein