110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

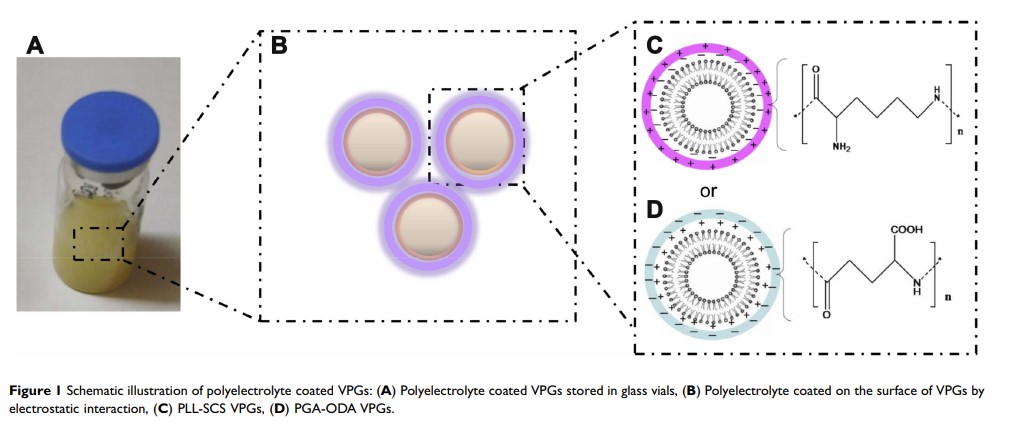
阳离子/阴离子聚电解质(PLL/PGA)薄膜包覆、装载阿糖胞苷的囊泡型磷脂凝胶(VPG)具有持续释放和抗神经胶质瘤的作用
Authors Qi N, Zhang Y, Tang X, Li A
Received 4 February 2020
Accepted for publication 9 April 2020
Published 12 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1825—1836
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S248362
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Cationic and anionic polymer-modified nanoparticles offer promising properties for the drug and gene delivery. Our study uses cationic/anionic polyelectrolyte coated vesicular phospholipid gels (VPGs) loaded with cytarabine (Ara-C) that enhance in vitro and in vivo anti-glioma effects.
Methods: Sodium cholesteryl sulfate (SCS) or octadecylamine (ODA) incorporated in a phospholipids phase were used to prepare charged VPGs, and cationic ϵ-polylysine (PLL) coated VPGs (PLL-SCS VPGs) and anionic γ-polyglutamic acid (PGA) coated VPGs (PGA-ODA VPGs) were prepared via electrostatic interactions, respectively. The morphology, particle size, zeta potential, rheology properties, and in vitro release were then characterized. The in vitro cytotoxicity and cellular uptake were evaluated on U87-MG glioma cells. The in vivo antitumor effects were studied on BALB/c nude mice bearing a right flank U87-MG glioma model.
Results: The TEM images and physicochemical properties of cationic/anionic polyelectrolyte coated VPGs exhibited that polymers covered on the vesicular surface. The results of rheologic property analysis showed that cationic/anionic polyelectrolyte coated VPGs enhanced the viscosity of uncoated VPGs. The in vitro release experiments revealed that cationic/anionic polyelectrolyte coated VPGs kept Ara-C sustained release up to 18 days. Specially, compared with PLL-SCS VPGs, PGA-ODA VPGs demonstrated higher in vitro cytotoxicity and cellular uptake efficiency in U87-MG glioma cells, and enhanced in vivo antitumor effects when subcutaneously injected around the tumor. No severe toxicity appeared in the right flank U87-MG glioma model of BALB/c nude mice.
Conclusion: Anionic γ-PGA coated VPGs were superior to cationic PLL coated VPGs in terms of improving the anti-glioma effect for local delivery.
Keywords: biodegradable depots, polyelectrolyte coating, sustained release, glioma, local therapy