110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-579-3p 通过抗炎症和抗凋亡在抗缺血性中风中具有神经保护作用
Authors Jia J, Cui Y, Tan Z, Ma W, Jiang Y
Received 1 December 2019
Accepted for publication 30 March 2020
Published 12 May 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1229—1238
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S240698
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Background/Aims: Multiple studies have found that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in the development of cerebral ischemia. MiR-579-3p can inhibit inflammatory responses and apoptosis, leading to ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) damage. However, the mechanism of how miR-579-3p actions in brain I/R injury remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism of the role of miR-579-3p in brain I/R injury.
Methods: A rat model of cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury was established by suture method. The effects of miR-579-3p on cerebral infarction size, brain water content, and neurological symptoms were evaluated. Flow cytometry was used to detect apoptosis. ELISA was used to detect the level of inflammatory factors. Western blot was used to detect the expression of P65, NCOA1, Bcl-2 and Bax. The relationship between miR-579-3p and NCOA1 was analyzed by bioinformatics analysis and luciferase assay.
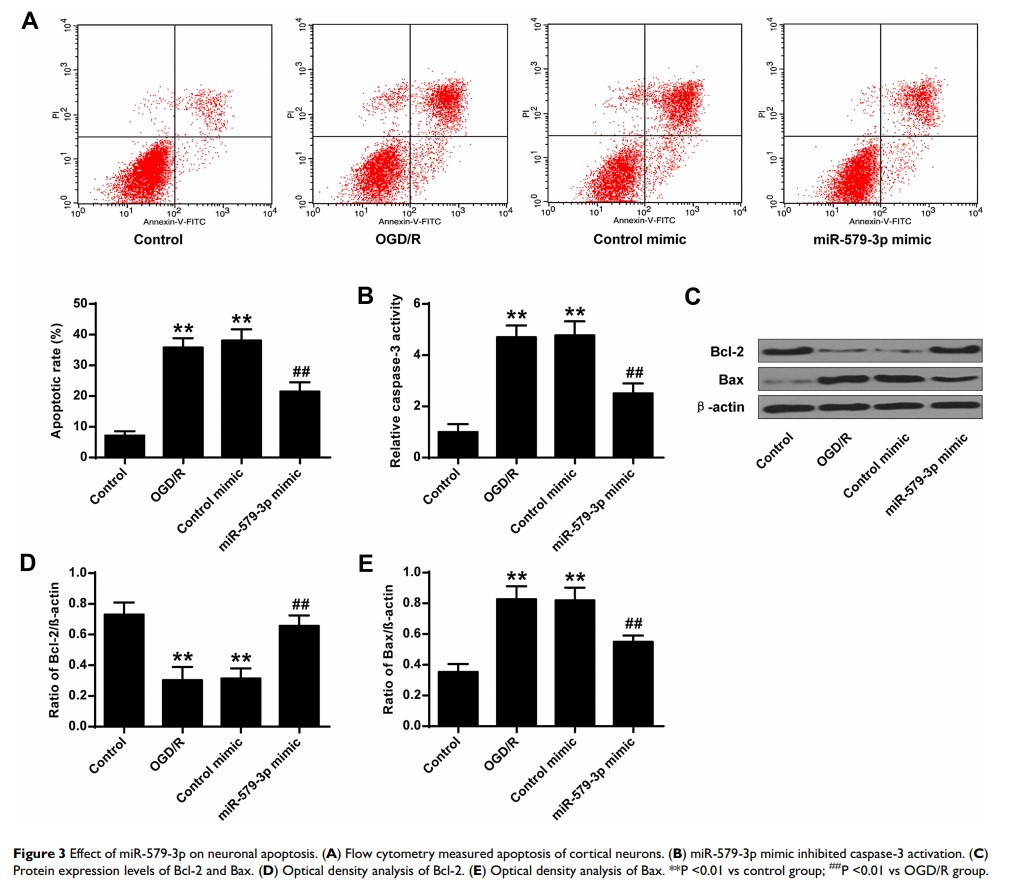
Results: Overexpression of miR-579-3p reduced infarct volume, brain water content and neurological deficits. Overexpression of miR-579-3p inhibited the expression level of the inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2 and iNOS, and increased the expression level of IL-10. MiR-579-3p overexpression inhibited NF-кB activity by reducing NRIP1. In addition, miR-579-3p could reduce the apoptotic rate of cortical neurons. Overexpression of miR-579-3p inhibited the activity of caspase-3, increased the expression level of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 in neurons, and decreased the expression level of apoptotic gene Bax.
Conclusion: miR-579-3p can be used to treat brain I/R injury, and its neuroprotective effect may be ascribed to the reduction of inflammation and apoptosis.
Keywords: ischemia/reperfusion, miR-579-3p, inflammation, apoptosis