110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

K-3-Rh 通过 PI3K-Akt 信号通路的抑制凋亡作用,保护大鼠免受脑缺血/再灌注损伤
Authors Sun J, Wang J, Hu L, Yan J
Received 6 October 2019
Accepted for publication 14 April 2020
Published 12 May 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1217—1227
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S233622
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Background/Aims: Ischemic stroke is the main cause of nerve damage and brain dysfunction, accompanied by strong brain cell apoptosis. This study aimed to investigate the effect of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (K-3-rh) on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury.
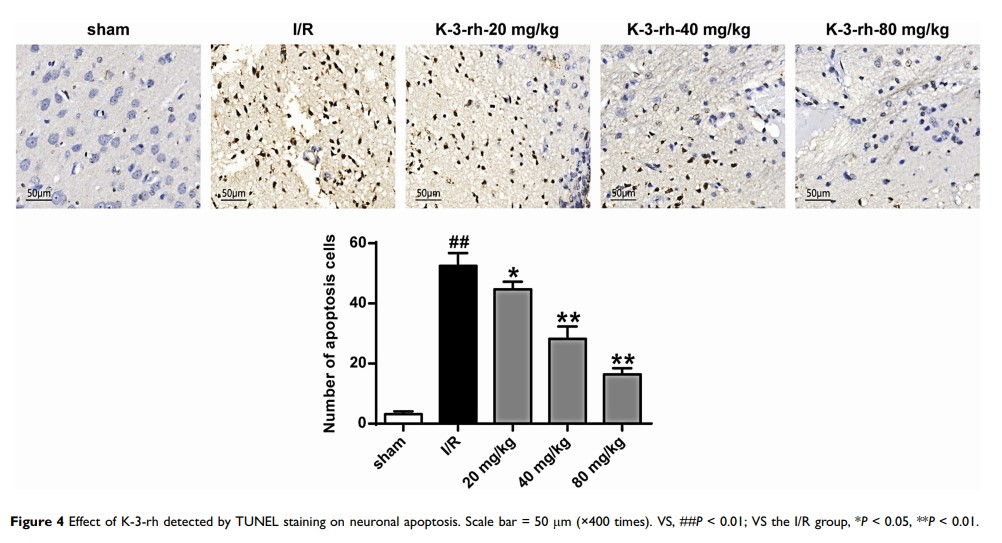
Methods and Materials: A rat model of cerebral I/R injury was established. The effects of K-3-rh on cerebral infarction size, brain water content and neurological deficits in rats were evaluated. Apoptosis of ischemic brain cells after mouse I/R was observed by TUNEL staining and flow cytometry. Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to detect the effect of K-3-rh on the expression of apoptosis-related proteins.
Results: K-3-rh can improve the neurological deficit score, reduce the infarct volume and brain water content, and inhibit cell apoptosis. In addition, K-3-rh significantly downregulated the expression of Bax and p53 and upregulated the expression of Bcl-2, and the phosphorylation level of Akt. Blockade of PI3K activity by the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin not only reversed the effects of K-3-rh on infarct volume and brain water content but also reversed the expression level of p-Akt.
Conclusion: K-3-rh had obvious neuroprotective effects on brain I/R injury and neuronal apoptosis, and its mechanism may be related to activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside, PI3K; Akt, apoptosis, cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury