110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

有 BRAFV600E 突变的甲状腺乳头状癌五级淋巴结转移预测因素和临床病理特征
Authors Li G, Tan H, Chen P, Hu HY, Liu M, Ou-yang D, Khushbu R, Pun D, Li J, Zhang Z, Yang Q, Huang P, Chang S
Received 3 February 2020
Accepted for publication 25 April 2020
Published 13 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3371—3378
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S247914
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Harikrishna Nakshatri
Background: Therapeutic lateral neck dissection (LND) is recommended in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients with clinically lateral lymph node metastasis (LLNM), whether underwent level V LND remains controversial for lacking of sensitive predicting system. BRAFV600E mutation is associated with aggressive tumor behavior, recurrence, and disease-specific mortality of PTC. However, the relationship between BRAFV600E mutation and level V LNM is unclear.
Methods: Univariate and multivariate analyses were retrospectively conducted on the potential predictive factors of 252 PTC patients who underwent initial treatment of neck lymph node dissection from September 2015 to October 2018 in our institute. BRAFV600E mutation and the clinicopathological characteristics of the two groups were compared.
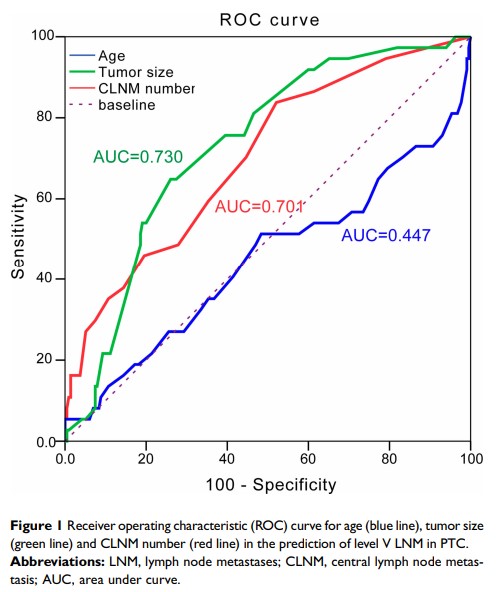
Results: LLNM was presented in 208 (82.5%) patients and level II–V LNM was present in 42.8%, 71.2%, 85.1%, 17.8% patients, respectively. BRAFV600E mutation was observed in 188 (74.6%) patients and was significantly associated with patients’ age, lymphocytic thyroiditis, capsule invasion, bilateral central lymph node metastasis (CLNM) and level V LNM in PTC. Univariate analysis revealed that lymphocytic thyroiditis, tumor size, number of CLNM, Level II LNM, Level III LNM, simultaneous Level II+III, simultaneous Level III+IV and simultaneous Level II+III+IV were significantly correlated with Level V LNM. In addition, multivariate analysis revealed that tumor size ≥ 2.5 cm, number of CLNM≥ 3, level II metastases and BRAFV600E mutation were independent Level V LNM predictors (odds ratio 3.910, 3.660, 8.410, 0.439; 95% CI 1.737– 10.135, 1.054– 12.713, 1.233– 57.355, 0.280– 0.827, respectively).
Conclusion: In summary, we presented several independent predictive factors for level V LNM in PTC patients. We constructed a risk prediction model consisting of tumor size ≥ 2.5 cm, number of CLNM≥ 3 and level II metastases and BRAFV600E mutation that may guide surgeons to evaluate the nodal status in PTC and perform tailored therapeutic LND.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, BRAFV600E mutation, level V lymph nodes metastasis, pathological features