110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

干扰宫颈癌细胞中人乳头瘤病毒 E6/E7 癌基因,可通过增加衍生自宫颈癌细胞的微囊泡中的 miR-377 抑制血管内皮细胞的血管生成
Authors Zhang Y, Liu Y, Guo X, Hu Z, Shi H
Received 25 November 2019
Accepted for publication 11 March 2020
Published 13 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4145—4155
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S239979
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
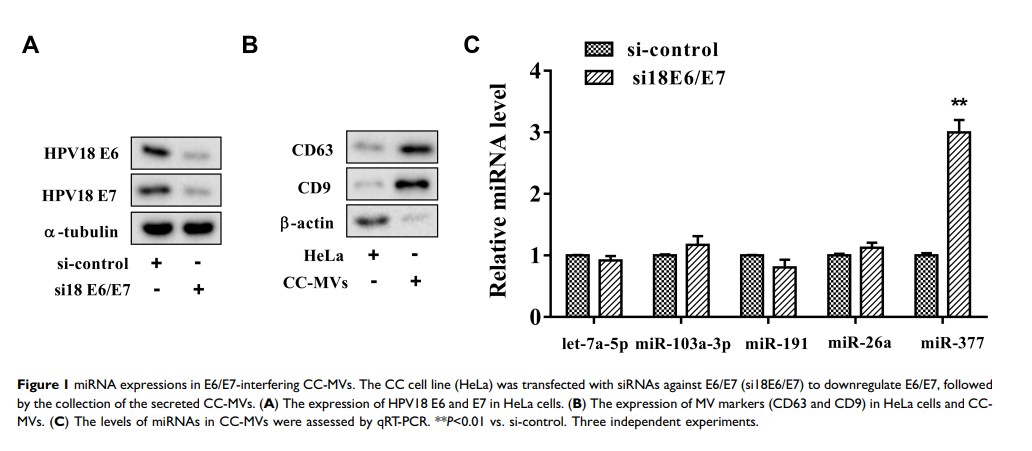
Background: The dysregulation of the human papillomavirus 18 E6 and E7 oncogenes plays a critical role in the angiogenesis of cervical cancer (CC), including the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of vascular endothelial cells. Interfering E6/E7 increases the number of CC cell-derived microvesicles (CC-MVs). Additionally, microRNAs (miRNAs) can modulate CC angiogenesis and can be encapsulated in MVs.
Objective: We aim to investigate whether E6/E7 affects CC angiogenesis via regulating miRNAs in CC-MVs.
Methods: CC-MVs were isolated from a CC cell line (HeLa) which were transfected with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) against E6/E7 or co-transfected with miR-377 mimics/inhibitors. The expression of several miRNAs in CC-MVs was detected using quantitative real-time PCR. After co-incubating CC-MVs with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation of HUVECs were determined using cell counting kit-8, transwell, and tube formation assays, respectively.
Results: MiR-377 was increased in E6/E7-interfering CC-MVs. Overexpressing miR-377 in CC-MVs suppressed HUVEC proliferation, migration, and tube formation. LPAR2, the cell surface G protein-coupled receptor, was the downstream target of miR-377 in HUVECs. The co-transfection of E6/E7 siRNAs and miR-377 inhibitors in CCs negated the effect of E6/E7 siRNAs on the elevation of miR-377 in CC-MVs. In HUVECs, the co-transfection of E6/E7 siRNAs and miR-377 inhibitors restored the LPAR2 expression which was reduced by the E6/E7 siRNA transfection. Meanwhile, miR-377 mimic reduced LPAR2 expression and inhibited HUVEC proliferation, migration, and tube formation, while such response was negated by LPAR2 overexpression.
Conclusion: Interfering E6/E7 increased miR-377 in CC-MVs, and overexpressing miR-377 in CC-MVs inhibited angiogenesis of HUVECs via reducing LPAR2.
Keywords: human papillomavirus E6/E7, microvesicle, miR-377, LPAR2, angiogenesis