110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于 UHPLC-MS/MS 和 UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS 的肾康注射液在大鼠体内的药代动力学和代谢研究
Authors Jiang X, Zhou L, Zuo L, Wang X, Shi Y, Du X, Zhang J, Liu L, Li Z, Xue L, Liu X, Sun Z
Received 22 October 2019
Accepted for publication 21 April 2020
Published 13 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1837—1850
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S235646
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Purpose: Shenkang injection, a traditional Chinese herbal prescription, had been widely used in renal disease due to its perfect curative effect. In this research, a novel, sensitive, accurate and rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method was developed to simultaneously detect the seven active ingredients in rat plasma of Shenkang injection and investigate its pharmacokinetic behaviors with metabolism profiling meanwhile.
Methods: For accurate pharmacokinetic quantitation, a WATERS ACQUITY UPLC® BEH C18 column was used to perform a separation and acetonitrile-water (0.1% formic acid) was selected as mobile phase for gradient elution with a flow rate of 0.20 mL/min. A heated electrospray ionization with selective reaction monitoring mode was used to monitor the precursor-product ion transitions for all the analytes and IS.
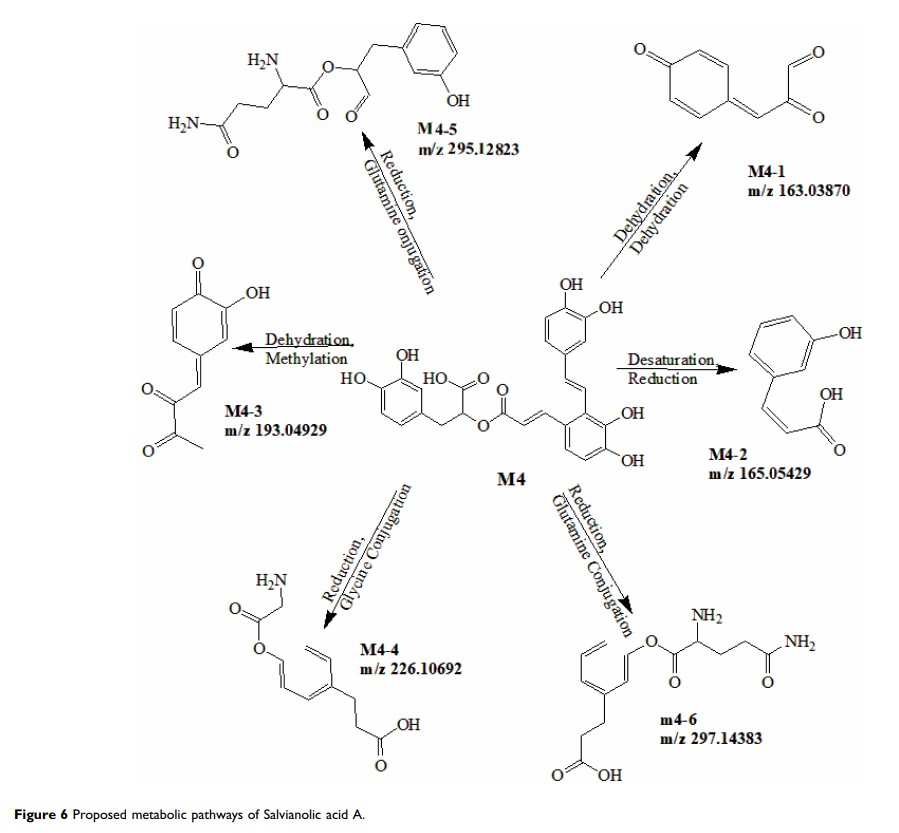
Results: They all showed good linearity over a wide concentration range (r > 0.996 3) and the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 0.1– 1.0 ng/mL for analytes. The validation parameters were all within the acceptable limits. Furthermore, for metabolism profiling study, metabolites of the seven ingredients were identified from the rat plasma based on the accurate mass and fragment ions. The metabolic pathways mainly focus on reduction, dehydration and conjugation.
Conclusion: This study provided an overview of disposition of Shenkang injection, which is highly instructive for better understanding the effectiveness and toxicity of this drug.
Keywords: Shenkang injection, pharmacokinetics, metabolism profiling, UHPLC-MS/MS, UHPLC-Q-orbitrap HRMS