110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国新医疗改革第一个十年(2009-2018)政府卫生支出分析:以新疆维吾尔自治区为例
Authors Feng C, Liang R, Jiang X
Received 5 March 2020
Accepted for publication 5 May 2020
Published 14 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 387—395
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S252652
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Objective: To analyze the status of government health expenditure in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region since the first 10 years from the new medical reform, and find the existing problems in order to provide evidence for the government to formulate medical and health policies.
Methods: Based on the health expenditure monitoring data of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region government from Urumqi Central Sub-branch of the People’s Bank of China, combined with the relevant data in Xinjiang statistical yearbook, Excel2013 and SPSS19.0 were used to conduct a comparative analysis of government expenditure data from 2009 to 2018.
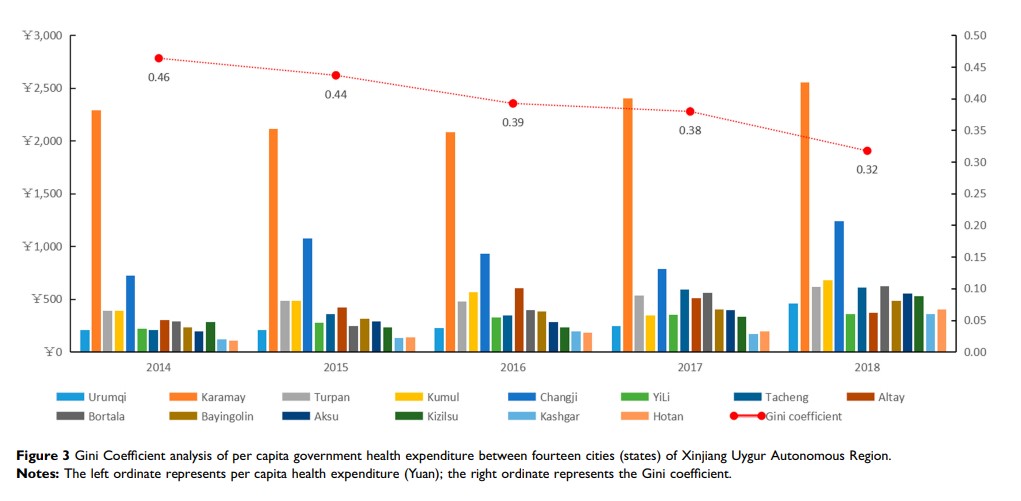
Results: The average annual growth rate of the government’s health expenditure in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region was 12.25%, which was similar to the national level. The proportion of government health expenditure in gross domestic product increased from 0.97% to 1.07%, while the proportion in the total fiscal expenditure decreased from 3.06% to 2.63%, which led to far behind the national and even western area level. The Gini Coefficient of per capita government health expenditure in every city (state) of the autonomous region fell from 0.46 to 0.32 between 2014 and 2018. In the past decade, the ratio between public health expenditure and medical institution expenditure has decreased from 1.01 to 0.42, led to insufficient proportion of public health expenditure. The health expenditure level of the four prefectures especially Kashgar and Hotan in Southern Xinjiang was still far lower than the whole autonomous region and the national average level.
Conclusion: The government of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region should continuously strengthen the financial expenditure in health, maintain the current situation of preferential policy implementation for rural and grassroots expenditure, constantly optimize the proportion of various financial expenditures, and strive for the transfer payment from the central and autonomous regional governments to the four prefectures in Southern Xinjiang.
Keywords: new medical reform, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, government finance, health