110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 HMGB1 的抑制可克服鼻咽癌对放疗和化疗的抵抗
Authors Zhu X, Cong J, Lin Z, Sun J, Yang B, Li A
Received 19 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 March 2020
Published 14 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4189—4199
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S239243
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
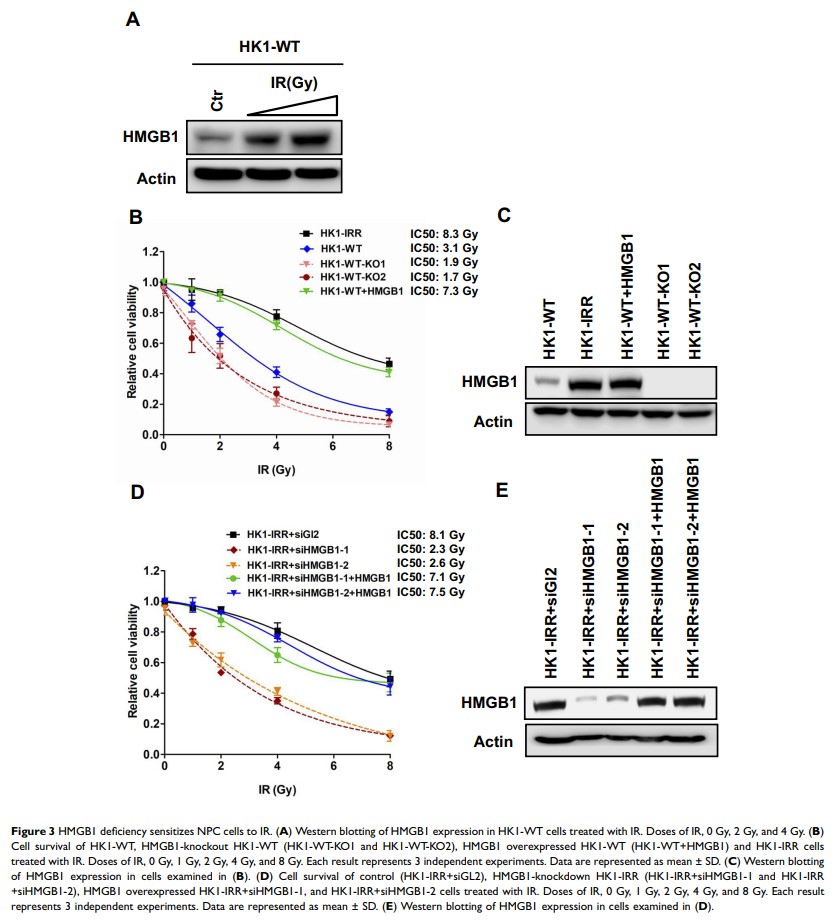
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effect of high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) on chemoresistance and radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Materials and Methods: HMGB1-knockout HK1 cell lines were generated using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system. Western blotting was used to evaluate the protein expression level of HMGB1. DNA repair efficiency of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) was monitored through NHEJ and HR reporter assay. Cellular protein–protein interaction between HMGB1 and NHEJ apparatus was determined by immunoprecipitation. Direct protein–protein interaction was examined by affinity capture assay with purified protein. Protein-DNA binding was evaluated by chromatin fractionation assay. Cell viability assay was employed to measure cell sensitivity to ionizing radiation (IR) or cisplatin.
Results: HMGB1-knockout NPC cells showed significant decrease in NHEJ efficiency. HMGB1 immunoprecipitated NHEJ key factors in NPC cells and promoted DNA-binding activity of Ku70. Mutational analysis revealed that serine 155 of Ku70 was required for its direct interaction with HMGB1. HMGB1 was highly expressed in radio- and chemoresistant NPC cells. Deficiency of HMGB1 sensitized wild-type (WT) and resistant NPC cells to IR and cisplatin. Glycyrrhizin, which is HMGB1 inhibitor, impaired DNA binding of HMGB1 and exhibited excellent synergy with IR and cisplatin.
Conclusion: HMGB1 promotes NHEJ via interaction with Ku70 resulting in resistance to IR and cisplatin. Inhibition of HMGB1 by glycyrrhizin is a potential therapeutic regimen to treat cisplatin and IR resistant NPC patients.
Keywords: NPC, HMGB1, NHEJ, resistance, Ku70, glycyrrhizin