110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DNMT1 通过下调 SMG1 增强 HPV 阳性头颈部鳞状细胞癌的放射敏感性
Authors Zhang C, Mi J, Deng Y, Deng Z, Long D, Liu Z
Received 15 August 2019
Accepted for publication 18 February 2020
Published 15 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4201—4211
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S227395
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Introduction: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), which rank the 7th malignant tumors worldwide, is closely related to methylation and HPV infection. Ionizing radiation therapy is the main strategy for HNSCC patients in advanced stage. Previously, HPV-positive HNSCC predict better prognosis than HPV-negative HNSCCs under radiotherapy, however its molecular mechanism is unresolved. SMG1 serves as a potential tumor suppressor in various cancers, including HNSCC.
Methods: The mRNAs and proteins expression of HPV E6/E7, p16, p53, DNMT1, SMG1 were detected after different treatments by qPCR and Western blot. The clone formation ability was measured in radiation dose after different treatments.
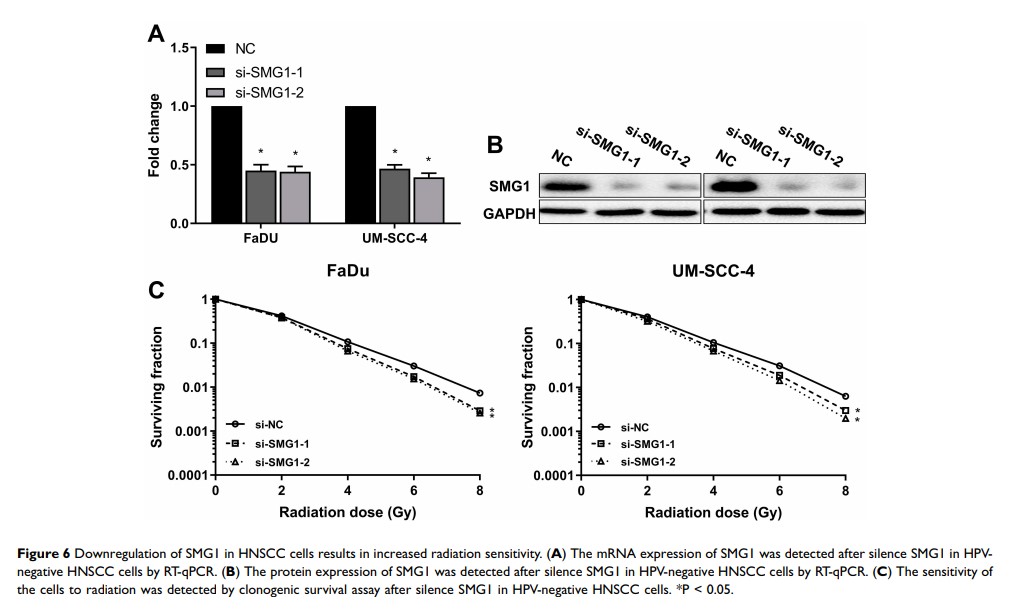
Results: In our study, the expression of HPV16 E6, DNA Methyltransferase 1(DNMT1) and SMG1 in head and neck carcinomas cell lines was detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. Forced E6 level in HPV-negative cells by overexpression plasmid promoted the expression of DNMT1, which resulted in decreased SMG1 expression. Silenced SMG1 in HPV-negative HNSCC cells elicited increased radiation sensitivity, suggesting that SMG1 may be an effective switch to regulate the effect of radiotherapy in HNSCC.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that DNMT1 enhances the radiosensitivity of HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas via downregulating SMG1.
Keywords: head and neck cancer, HPV, DNMT1, SMG1, radiotherapy