110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过靶向 FOXP1,MicroRNA-374b-5p 在非小细胞肺癌中起到肿瘤抑制剂的作用,并可预测癌症患者的预后
Authors Li J, Zhang X, Tang J, Gong C
Received 20 December 2019
Accepted for publication 7 April 2020
Published 15 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4229—4237
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S243221
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Lung cancer remains the most frequent malignancy worldwide with increasing morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to assess the expression of microRNA-374b-5p (miR-374b-5p) in tissues and cell lines of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and to evaluate the prognostic value of miR-374b-5p as well as its biological function in tumor progression.
Materials and Methods: Expression of miR-374b-5p in NSCLC patients and cells was estimated using quantitative real-time PCR. The prognostic value of miR-374b-5p was evaluated using Kaplan–Meier method and Cox regression analysis. Gain-of-function and loss-of-function cell experiments were performed to examine the effects of miR-374b-5p on NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. A luciferase activity assay was used to confirm the target gene of miR-374b-5p.
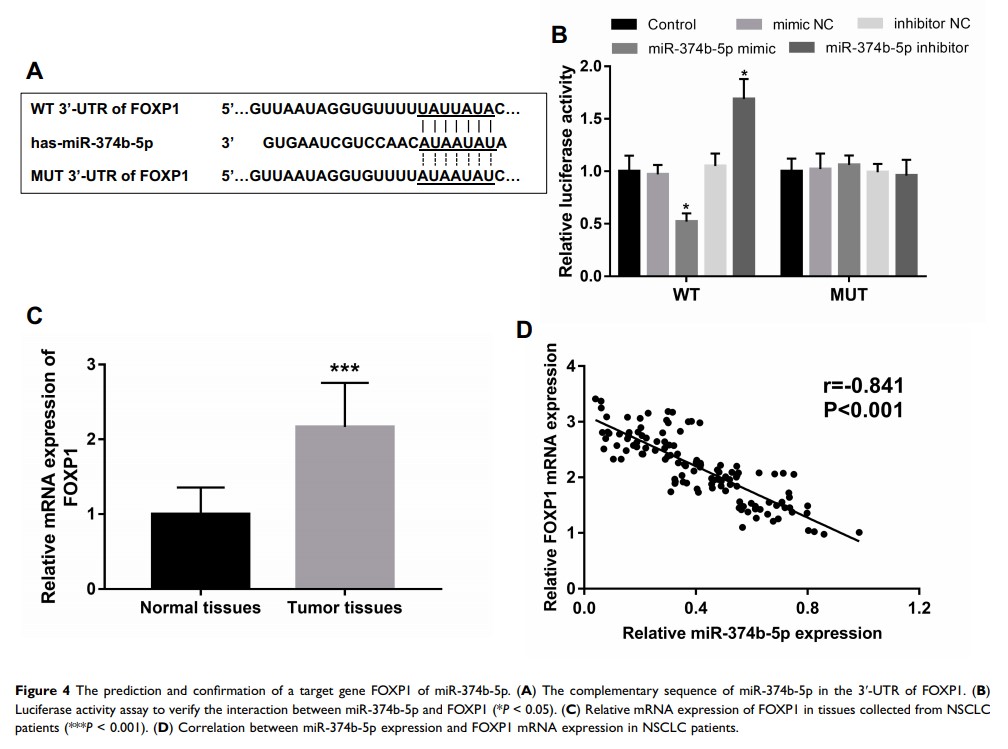
Results: miR-374b-5p expression levels were decreased in tumorous tissues and cell lines compared with the normal tissues or cells (P < 0.05). The expression of miR-374b-5p was associated with the patients’ tumor size, lymph node metastasis and TNM stage (all P < 0.05). Patients with low miR-374b-5p expression have a shorter survival time (log-rank P = 0.001), and the downregulated expression of miR-374b-5p was determined to be an independent prognostic indicator of NSCLC. In NSCLC cells, the overexpression of miR-374b-5p could inhibit NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion and could directly target FOXP1.
Conclusion: This study found that the decreased miR-374b-5p predicts poor prognosis of NSCLC, and the upregulation of miR-374b-5p can inhibit NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. The data obtained from this study provide a novel candidate prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, microRNA-374b-5p, prognosis, proliferation, migration, invasion