110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

阿帕替尼治疗无法手术的转移性或局部晚期软骨肉瘤:我们从两中心研究中可以了解哪些软骨肉瘤的生物学行为
Authors Xie L, Xu J, Sun X, Liu K, Li X, He F, Liu X, Gu J, Lv Z, Yang R, Tang X, Yan T, Li D, Yang Y, Dong S, Sun K, Shen D, Guo W
Received 10 March 2020
Accepted for publication 5 May 2020
Published 15 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3513—3525
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S253201
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Purpose: For patients who have chondrosarcoma in the unresectable setting, antiangiogenic agents are reportedly effective. This multicenter, retrospective study investigated the antitumor activity of apatinib in patients with unresectable chondrosarcoma to gain insight into the biological behavior of this disease.
Methods: All of the patients with unresectable chondrosarcoma who were diagnosed between October 1, 2009, and November 1, 2019, in two sarcoma centers affiliated with Peking University were evaluated. Relevant information was collected from the medical records at both centers, from which patients receiving apatinib for systemic therapy were selected for analysis.
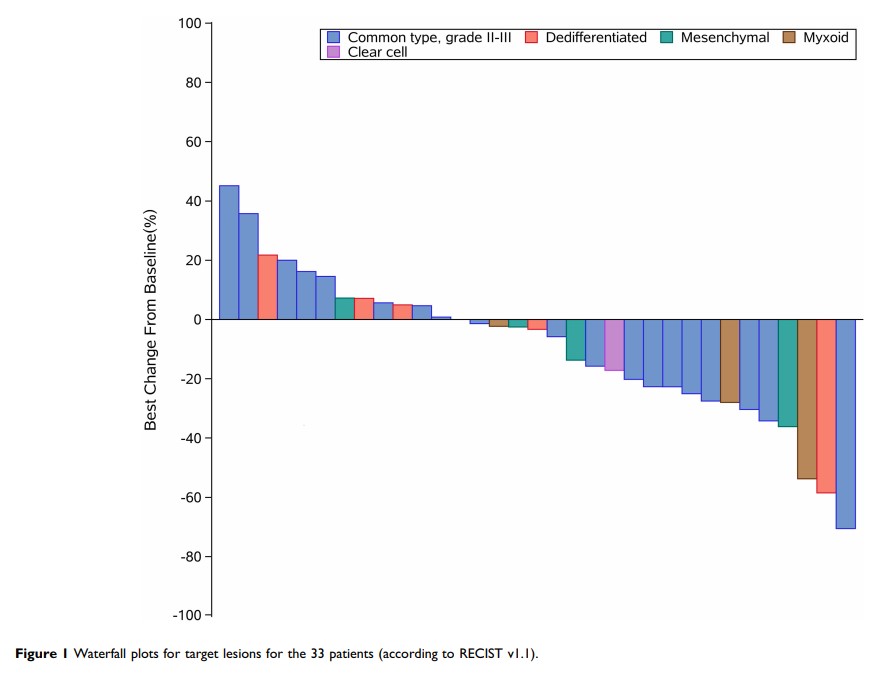
Results: In total, efficacy analysis was conducted in 33 patients with a median follow-up time of 22.1 (Q1, Q3, 14.6, 23.0) months. There were 20/33 (60.0%) conventional chondrosarcomas (grades 2– 3), 5/33 (15.2%) dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas, 4/33 (12.1%) mesenchymal chondrosarcomas, 3/33 (9.1%) extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, and 1/33 (3.1%) clear-cell chondrosarcomas with 87.9% in metastatic and 12.1% in locally advanced states. The objective response rate was 6/33 (18.2%). The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.4 months (Q1, Q3, 7.0, 21.2), while the median overall survival has not yet been reached. Rare variants of chondrosarcoma tended to have a longer PFS than conventional chondrosarcoma (P =0.06). Based on clinicopathological factors Cox and univariate analysis, only extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma and baseline target lesions < 60 mm benefited from the drug apatinib (P =0.14 and P =0.00), respectively. Grade 3 or higher adverse events were frequent in 11/33 (39.3%) of patients who discontinued apatinib due to deterioration of their general condition.
Conclusion: Apatinib had clinically meaningful activity in patients with inoperable high-grade chondrosarcoma. However, special caution should be made in managing toxicity due to the indolent behavior and slow growth pattern after using this drug. Patients with a smaller tumor size and extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma subtype might benefit from this therapy more.
Clinical Trial Registration: Registered February 7, 2020, with clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04260113.
Keywords: chondrosarcoma, apatinib, inoperable, metastasis, locally advanced