110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SPOCK1 参与上皮-间质转化: 癌症治疗的新靶标?
Authors Sun L, Li S, Guo Q, Zhou W, Zhang H
Received 14 February 2020
Accepted for publication 22 April 2020
Published 18 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3561—3569
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S249754
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yong Teng
Background: Cancer metastasis is the main obstacle to increasing the lifespan of cancer patients. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a significant role in oncogenic processes, including tumor invasion, intravasation, and micrometastasis formation, and is especially critical for cancer invasion and metastasis. The extracellular matrix (ECM) plays a crucial role in the occurrence of EMT corresponding to the change in adhesion between cells and matrices.
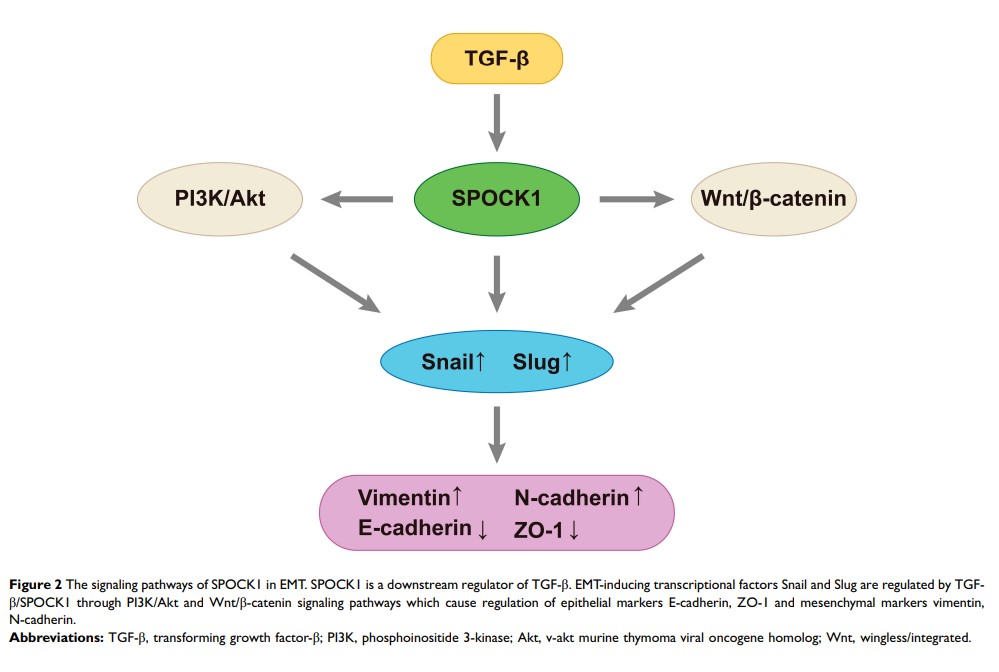
Conclusion: SPOCK1 is a critical regulator of the ECM and mediates EMT in cancer cells. This suggests an important role for SPOCK1 in tumorigenesis, migration and invasion. SPOCK1 is a critical regulator of some processes involved in cancer progression, including cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration. Herein, the functions of SPOCK1 in cancer progression are expounded, revealing the association between SPOCK1 and EMT in cancer metastasis. SPOCK1 is a positive downstream regulator of transforming growth factor-β, and SPOCK1-mediated EMT regulates invasion and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. It is of significance that SPOCK1 may be an attractive prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in cancer treatment.
Keywords: SPOCK1, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, extracellular matrix, cancer, metastasis