110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

香叶木素抑制肝癌中的细胞增殖、诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期阻滞
Authors Ma A, Zhang R
Received 26 November 2019
Accepted for publication 8 April 2020
Published 18 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3537—3546
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S240064
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Objective: Diosmetin (DIOS) has been confirmed to possess anti-cancer effects in some types of tumors. However, it remains unclear whether DIOS exerts anti-cancer effects on liver cancer. Thus, our purpose was to observe the effect of DIOS on cell proliferation, cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human liver cancer cells.
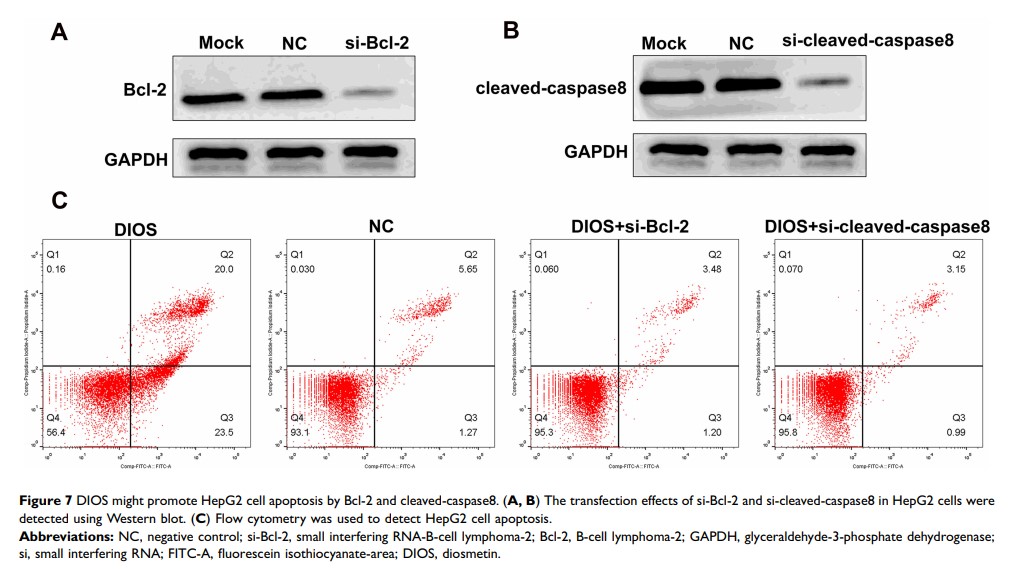
Materials and Methods: The cell viability of HepG2 and HCC-LM3 cells under different concentrations of DIOS was detected using MTT assay. The cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest were analyzed by flow cytometry. The expression levels of apoptosis/cell cycle-related proteins including P53, Bcl-2, Bax, cleaved-caspase3, cleaved-caspase8, cleaved-PARP, Bak, cdc2, cyclinB1 and P21 were measured using Western blot. HepG2 cells were transfected by checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1)-small interfering RNA (siRNA) and checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2)-siRNA, respectively. After that, cell cycle was detected.
Results: DIOS significantly suppressed cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis of HepG2 cells and HCC-LM3 cells. Moreover, DIOS promoted cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase. Western blot results showed that DIOS significantly suppressed the expression levels of Bcl-2, cdc2, cyclinB1, and promoted the expression levels of Bax, cleaved-caspase3, cleaved-caspase8, cleaved-PARP, Bak, P53, and P21. The G2/M phase arrest was observed in HepG2 cells transfected with Chk2-siRNA, while the G2/M phase arrest was not obvious in HepG2 cells transfected with Chk1-siRNA.
Conclusion: Our findings revealed that DIOS could inhibit cell proliferation and promote cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in liver cancer. Furthermore, DIOS could induce G2/M cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cell via targeting Chk2.
Keywords: diosmetin, cell apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, liver cancer, HepG2 cell