110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

H2A.Z 亚型在肝细胞癌中的重要和独特作用
Authors Tang S, Huang X, Wang X, Zhou X, Huang H, Qin L, Tao H, Wang Q, Tao Y
Received 26 December 2019
Accepted for publication 9 April 2020
Published 18 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 4319—4337
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S243823
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Purpose: H2A.Z is an oncogenic histone variant that is overexpressed in cancers. Two isoforms of H2A.Z, H2AFZ and H2AFV, are identical except for a three-amino acid difference. However, their isoform-specific functions remain unclear in cancer development. Thereby, this study aimed to investigate whether the two isoforms play distinct functions in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Materials and Methods: Expressions of H2A.Z isoforms in 116 paired hepatocellular cancerous and para-cancerous tissues were detected by employing qPCR. GEO and TCGA databases were used to probe expressions and prognostic value of the two H2A.Z isoforms. A comprehensive meta-analysis was conducted. Furthermore, co-expressed analysis of H2AFZ and H2AFV was performed by using cBioPortal database. H2A.Z binding genes from Chip-seq were intersected with H2A.Z isoforms co-expressed genes to perform functional annotations. Cell proliferation experiments from H2AFZ knockout HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells were implemented. Finally, RNA-seq was applied to analyse alternative splicing in H2AFZ knockout and wild-type cells.
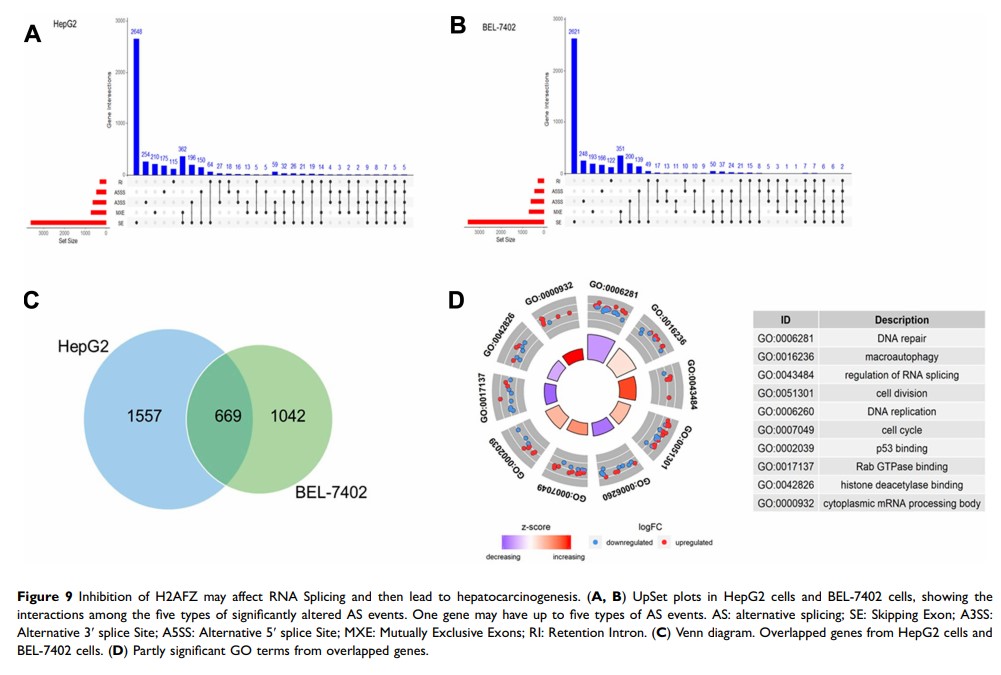
Results: H2AFZ and H2AFV were both significantly upregulated (P < 0.01) in hepatocellular carcinoma and related to poor prognosis (P < 0.01). The two H2A.Z isoforms played vital roles in cell proliferation. It is also predicted that unique functions of H2AFV contain spindle midzone and microtubule, while H2AFZ is especially associated with RNA export and spliceosome. Further, devoid H2AFZ may restrain liver cancer cell proliferation and cause many alternative splicing events.
Conclusion: Both H2A.Z isoforms play vital and distinct roles in the occurrence and progression of liver cancer, which may pave a way for novel therapeutic applications for cancers in the future.
Keywords: H2A.Z, H2AFV, H2AFZ, hepatocellular carcinoma, functional annotations, distinct roles