110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

来氟米特通过遏制人膀胱癌细胞的自噬和 PI3K/Akt 信号通路抑制增殖并诱导细胞凋亡
Authors Cheng L, Wang H, Wang Z, Huang H, Zhuo D, Lin J
Received 5 March 2020
Accepted for publication 7 May 2020
Published 18 May 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1897—1908
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S252626
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Introduction: Bladder cancer is a lethal human malignancy. Currently, treatment for bladder cancer is limited. The anti-tumor effects of leflunomide have attracted much more concern in multiple human cancers.
Materials and Methods: This study evaluated the anti-tumor effects of leflunomide on cell viability, colony formation, apoptosis, and cell cycle in two human bladder carcinoma cell lines, 5637 and T24. Meanwhile, the underlying mechanism including PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and autophagy modulation was also identified.
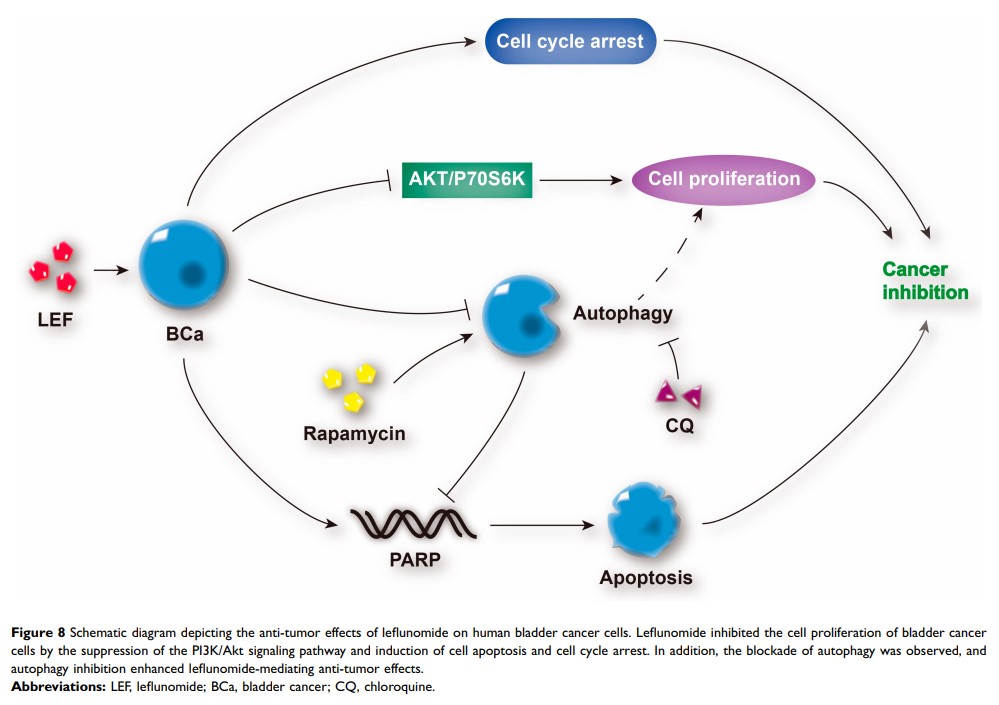
Results: Leflunomide markedly inhibited the growth of both bladder cancer cell lines and induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in S phase. The phosphorylation levels of Akt and P70S6K in both cell lines were significantly down-regulated with leflunomide treatment. Furthermore, the deceased formation of autophagosomes and the accumulation of LC3II and P62 suggested the blockade of autophagy by leflunomide. Modulation of autophagy with rapamycin and chloroquine markedly attenuated and enhanced the cytostatic effects of leflunomide, respectively.
Conclusion: Leflunomide significantly reduced the cell viability of bladder cancer cells via inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and suppressing the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. In addition, the blockade of autophagy was observed, and autophagy inhibition enhanced leflunomide-mediating anti-tumor effects. Our data presented here offer novel ideas for comprehensive therapeutic regimes on bladder cancer.
Keywords: leflunomide, autophagy, PI3K/Akt pathway, anti-tumor, bladder cancer