110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

质粒编码的 blaNDM-5 基因使源自猪肉的鼠伤寒沙门氏菌具有高水平的碳青霉烯类耐药性
Authors Gao Y, Wen J, Wang S, Xu X, Zhan Z, Chen Z, Bai J, Qu X, Zhang H, Zhang J, Liao M
Received 11 February 2020
Accepted for publication 28 April 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1485—1490
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S249357
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sahil Khanna
Purpose: Carbapenem resistance is rarely reported in Salmonella Typhimurium, especially from a food origin. Here, we report a plasmid-mediated mobile carbapenem-resistant blaNDM-5 gene in Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from pork in Shanghai, China in 2016.
Patients and Methods: In July 2016, the S . Typhimurium SH160 strain was recovered from minced pork meat purchased from a supermarket in Yangpu District, Shanghai, China. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing, multi-locus sequence typing, conjugation, S1-PFGE, southern hybridization, whole-genome sequencing and data analysis were performed.
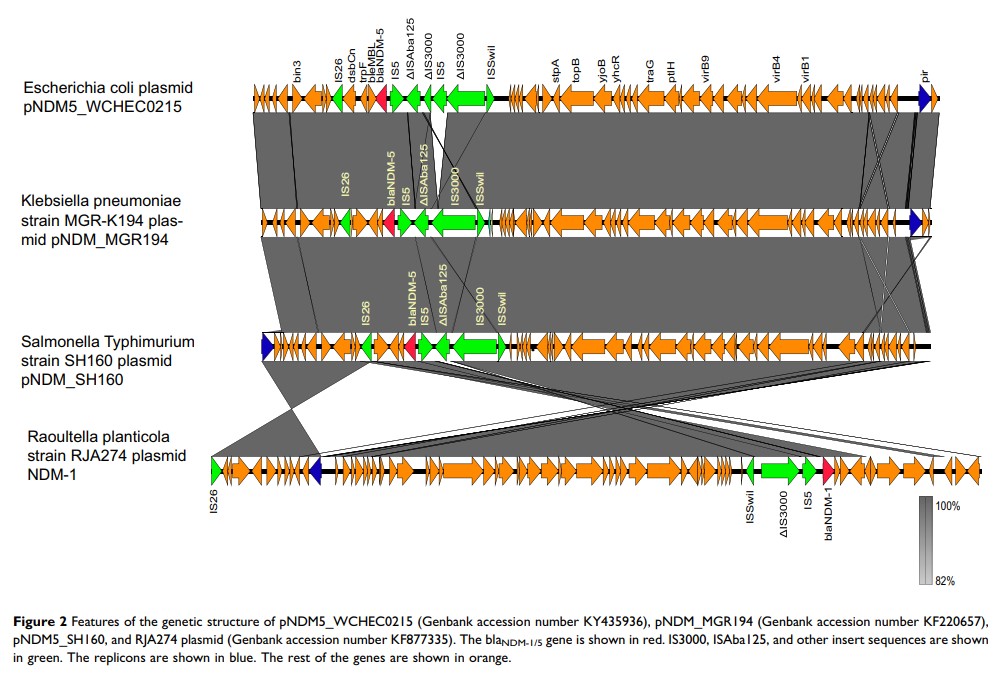
Results: This isolate was found to be a ST34 strain and resistant to carbapenems, cephalosporins, and most other commonly used antibiotics. The blaNDM-5 gene was harbored by a 46161-bp IncX3 plasmid which was found to be transferable. The IncX3 plasmid contains a composite cassette, consisting of ISSwil-IS3000-ΔISAba125-IS5-blaNDM-5 -bleMBL-trpF-dsbC-IS26-ctuA1-ΔumuD . In addition, this strain was found to harbor an additional 161706-bp IncHI2 plasmid which carries nine resistant genes, such as aadA1, aadA3, aph(3 ʹ )-la, sul1, sul2, sul3, floR, cmlA and dfrA12 .
Conclusion: We reported the S. Typhimurium with transferable IncX3 plasmid harboring blaNDM-5 gene from minced pork. We characterized the complete genetic features of the plasmid, which demonstrated the potential for spreading in different bacterial pathogens. Therefore, extensive surveillance and monitoring for carbapenem-resistant bacterium in the food chain and public health are urgently required.
Keywords: S . Typhimurium, pork, blaNDM-5 , public health