110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

驱动蛋白超家族成员 2A(KIF2A)的过表达与食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖和预后有关
Authors Li D, Sun H, Meng L, Li D
Received 1 February 2020
Accepted for publication 23 April 2020
Published 20 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3731—3739
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S248008
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
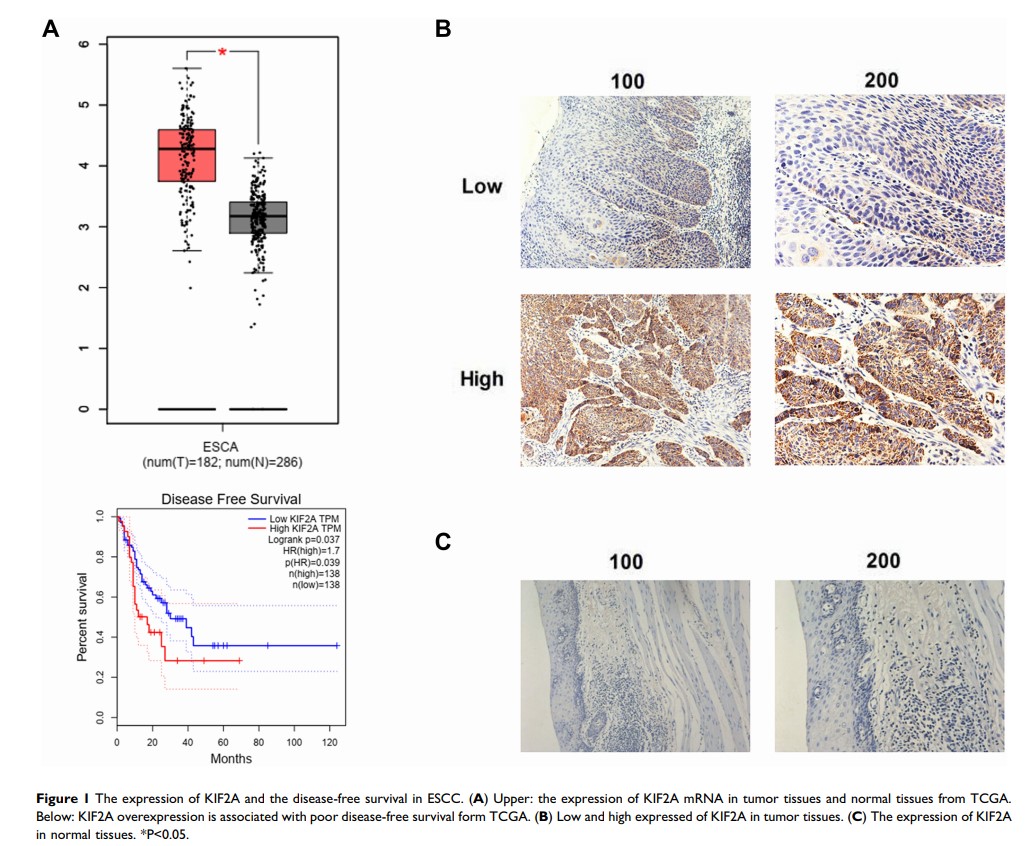
Aim: Kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) is a member of the kinesin-13 superfamily protein. KIF2A played a role in the development of many tumors. However, the role of KIF2A in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of KIF2A in ESCC.
Methods: We used bioinformatics analysis to study the expression levels and prognosis of KIF2A in ESCC and normal tissues. We also used our own samples to verify the results by immunohistochemistry. Then, the biological functions of KIF2A in ESCC was studied by cell experiments and animal experiments.
Results: Both the TCGA database and our samples showed that KIF2A was relatively highly expressed in ESCC tissues and was significantly associated with disease-free survival (P =0.037) in TCGA database. Colony formation assay, CCK8 and Western blotting results showed that knockdown of KIF2A can significantly reduce colony forming ability and proliferation ability. The results of animal experiments showed that knocking down KIF2A can significantly reduce the tumor volume of mice.
Conclusion: KIF2A might be used as a prognostic factor for ESCC, and knockdown of KIF2A could inhibit ESCC proliferation in vitro and in vivo, respectively. KIF2A could serve as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for future ESCC.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, kinesin superfamily protein 2A, ESCC, KIF2A, proliferation